Climate
All Climate Content
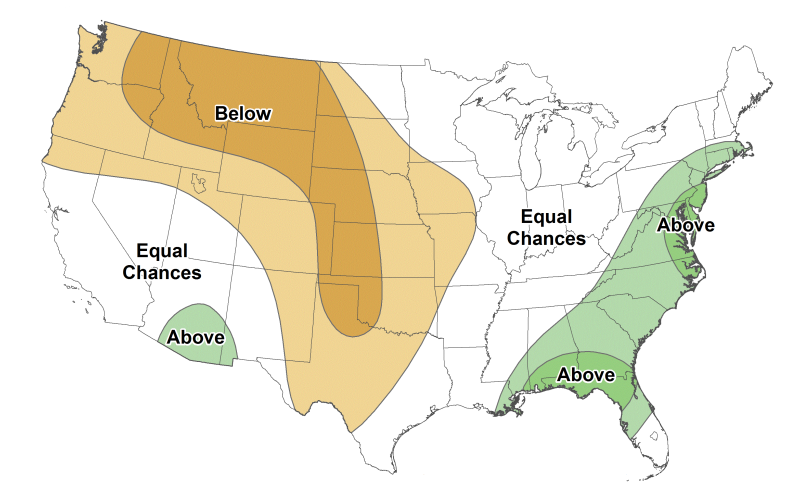
2022 Summer Climate and Drought Outlook
On May 19, the NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center released their temperature and precipitation outlooks for June and the summer season ahead. See a full report of what to expect for the summer of 2022.
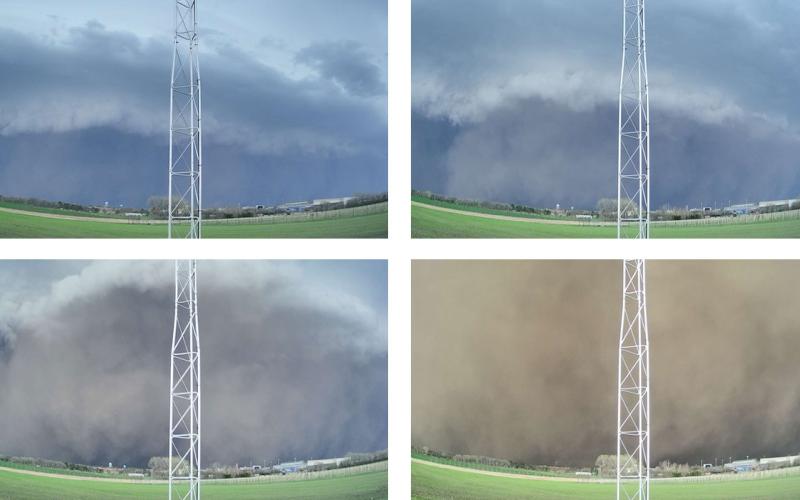

What is a derecho?
In the aftermath of the May 12, 2022 derecho that impacted eastern South Dakota, many are wondering what derechos are and what conditions can cause them.
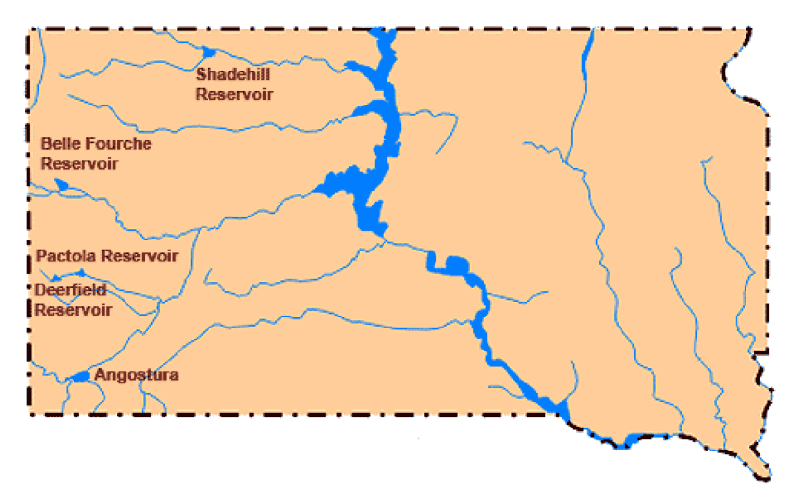
Spring Storms Help Bureau of Reclamation Reservoirs in Northwestern South Dakota
While the moisture was needed, the systems were severe with blizzard conditions occurring from multi-day, strong-gusting winds across the area.
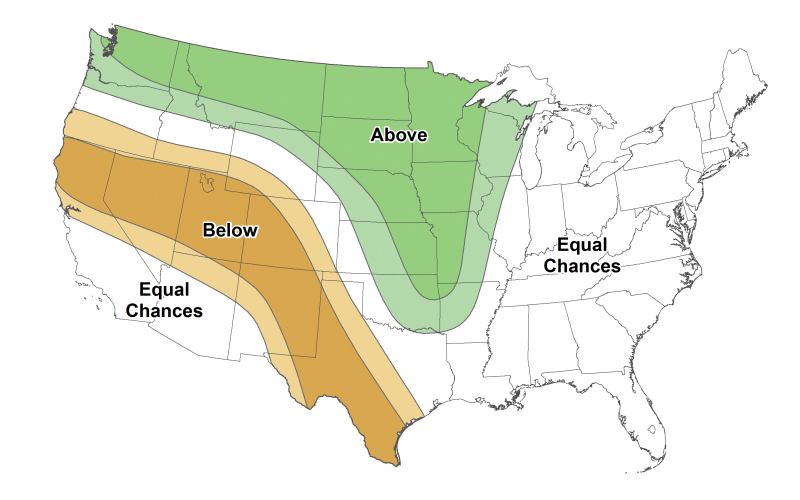
May 2022 Drought and Climate Outlook
The May climate outlook favors cooler and wetter than average conditions. It is possible producers could experience some short-term drought relief, with a return to drought or re-intensifying in the mid-summer season.
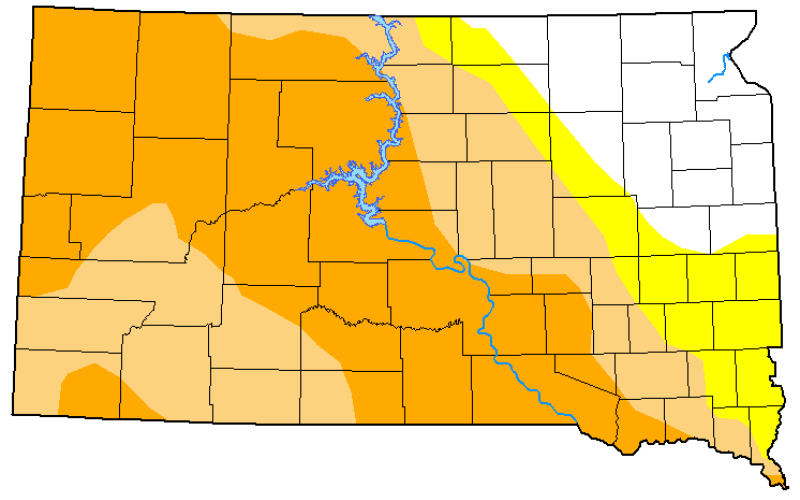
Drought
Stay ahead of drought impacts with SDSU Extension's timely climate updates, business insights and research-tested management tips.

Temperature and Herbicide Performance
In South Dakota, the spring can come with a wide range of temperature fluctuations. This will affect the performance of burndown herbicides. Depending upon the target weed, type of herbicide and application rate, there will likely be decreased weed control in cooler temperatures.
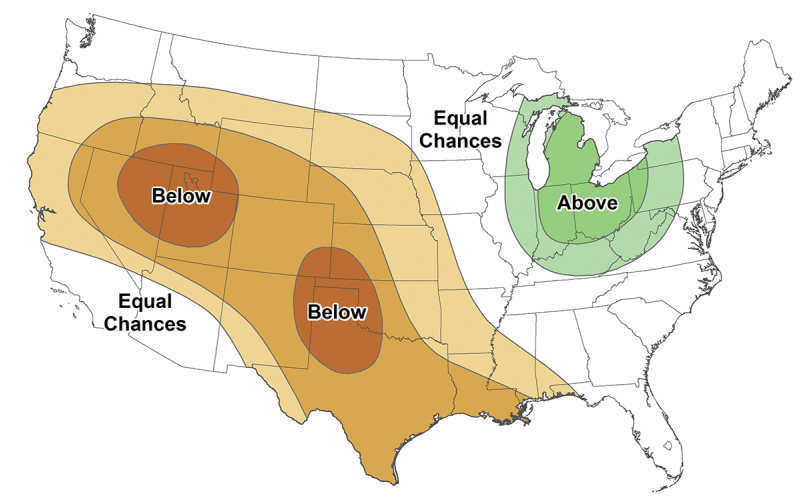
Drought Concerns Continue With 2022 Spring Climate Outlook
March 23, 2022
The climate outlook for spring 2022 has increased concern for drought in South Dakota, with the March 17 U.S. Drought Monitor showing two-thirds of the state in either moderate or severe drought.
The Fusarium Head Blight Prediction Tool
The Fusarium head blight prediction tool, available through Penn State University and Mesonet at SDState, uses weather variables to predict the risk for Fusarium head blight in wheat.

Pre-Plant Disease Management Considerations
If the forecast holds true, it looks like it is going to be another year of excessive soil moisture and possible flooding come this spring. The increased level of soil moisture has implications with regards to plant stand establishment as well as root rot and nematode infestations.
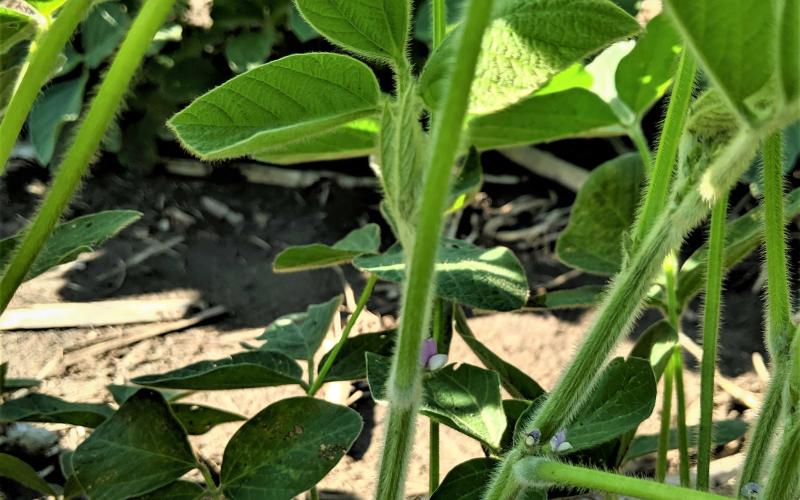

Current Weather Conditions Are Conducive White Mold Development in Soybeans
Frequent rains and overcast conditions continue to occur in South Dakota’s main soybean growing counties. These conditions favor white mold development. In some of these counties, soybean is already at R1, which is also the best timing for fungicide application targeting white mold control.