Crop Management
All Crop Management Content

Davis retires after 30 years with SDSU Extension
July 17, 2024
South Dakota State University Extension Crops Business Management Specialist Jack Davis is retiring after 30 years of serving South Dakota’s agricultural community.

SDSU Northeast Research Farm reschedules field day to July 18
July 11, 2024
Northeast Research Farm by South Shore has rescheduled its field day to July 18, 2024.

SDSU Extension hosting Integrated Pest Management Field School
July 08, 2024
South Dakota State University Extension will host an Integrated Pest Management Field School on July 23, 2024, by Volga.

Critical Period of Weed Control: A good, but not perfect guideline
The critical period of weed control is the period during a crop lifecycle when weeds need to be managed to avoid a significant yield loss.

Current State of Noxious Weed Management in South Dakota
Results of an online survey to determine how South Dakota stakeholders are currently managing noxious weeds.
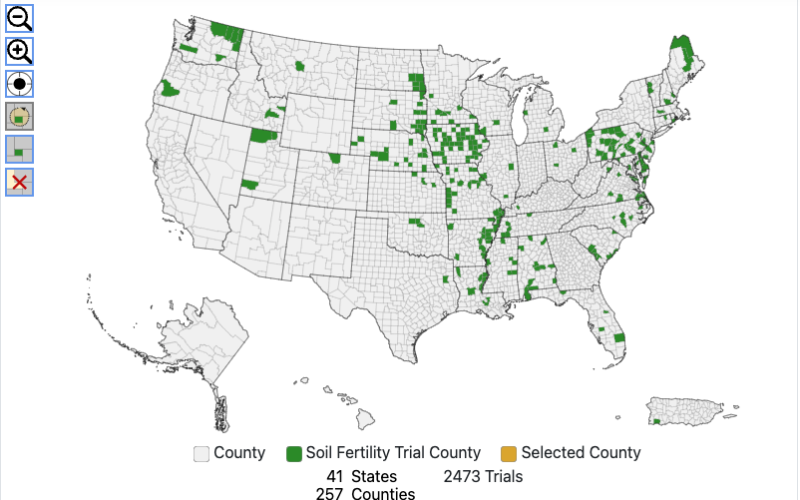
New digital Fertilizer Recommendation Support Tool launches nationwide
April 11, 2024
South Dakota State University Extension and project partners are proud to announce the nationwide release of the Fertilizer Recommendation Support Tool (FRST), a decision aid that provides an unbiased, science-based interpretation of soil phosphorus and potassium values for crop fertilization.

Herbicide Carryover Concerns for 2024
Herbicides with residual activity have great utility for weed management. However, due to environmental conditions, some herbicides can persist so that the crop grown next year can be injured.

Conservation Practices Increasing in South Dakota
The recently released Agricultural Census data of 2022 shows that the share of cropland acres under conservation practices has continued to increase in South Dakota.

Proso Millet Trial Results
In 2020, proso millet trials were conducted in 1 location in South Dakota.

Barley Variety Trial Results
In 2019, Barley trial was planted at one location in South Dakota.