Content by Tong Wang

S.D. Producers’ Willingness To Adopt Patch Burn Grazing vs. Winter Patch Grazing
Patch-burn grazing and winter patch grazing are heterogenous rangeland management practices that aim to increase the variety of grass composition to benefit wildlife and maintain livestock production. To learn about producers’ desire to adopt these practices, we conducted an online survey between November 2019 and January 2020.

Producer Views on Patch Burn Grazing vs. Winter Patch Grazing in S.D.
Traditional rangeland management promotes uniform forage utilization, yet causes detrimental effects on the richness of plant species and wildlife habitat. Therefore, management practices that increase heterogeneity in vegetation play an important role in developing habitat types and preserving grassland wildlife species.

Barriers To Rotational Grazing: Perceptions From Ranchers in the Dakotas
Despite the potential benefits of rotational grazing, its adoption rate has stagnated in recent years. To help understand major barriers faced by producers towards rotational grazing, we conducted a survey among ranchers in the U.S. Great Plains.
South Dakota Ag Land Soil Tables Tool
The Ag Land Soil Tables Tool allows users to view soil data and download data by county to further understand the soil rating system. It can help appraisers make baseline agricultural land assessments and determine if adjustments from baseline are needed.

Utilizing Cover Crops for Grazing: An Assessment on Economic Benefits
Grazing cover crops by cattle provides an option to offset cover crop seed costs and increase farm revenue. To facilitate farmers’ decision making, this article will evaluate the economic profitability from grazing cattle on cover crops using a partial budgeting approach.

Rotational Grazing Improves Stocking Capacity and Ranch Profitability
Livestock stocking rate is considered as one of the most important decisions that ranchers can make, as heavy stocking rate causes grassland degradation and adversely impact the sustainable delivery of ecosystem services.

Farm Practices That Improve Soil Health: Integrated Crop-Livestock Systems
An integrated crop-livestock system can provide an alternative management strategy that benefits producer’s income, soil health, and the environment—all while increasing production.

Farm Practices That Improve Soil Health: Cover Crops and Crop Residues
Planting cover crops and returning crop residues (stover) to the soil both adds nutrients and improves overall soil quality. These practices are common with producers across South Dakota and have been recently studied by researchers to identify how they impact the release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
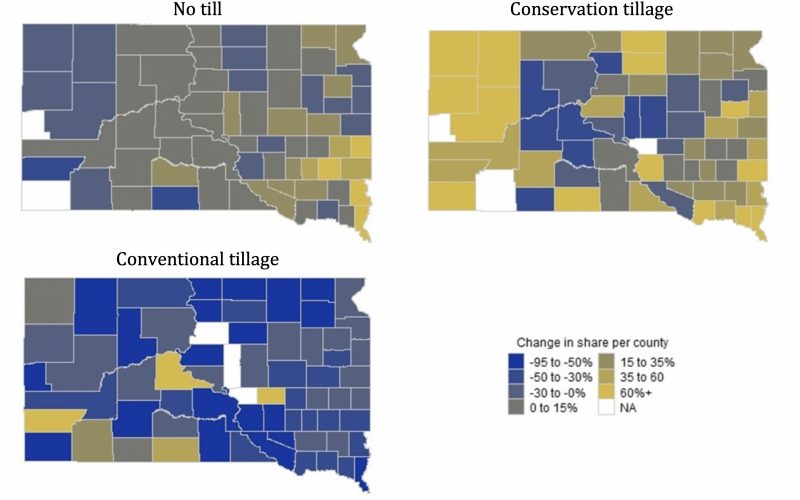
Soil Conservation Practice Adoption Status at the S.D. County Level: 2012–2017
An increasing number of farmers across the state of South Dakota have adopted different soil conservation practices such as no-till, conservation tillage and cover crops. Over time, these practices play significant roles in improving soil health and increasing soil resilience towards extreme weather conditions.

Large Farms More Dominant in South Dakota Crop Production
Large farms play a more dominant role in South Dakota crop production, according to the recently released 2017 U.S. Census of Agriculture. As of 2017, large farms of more than 2,000 acres operate 66.8% of South Dakota total cropland aces compared to 47.7% as of 1997.