Planting Wheat
All Planting Wheat Content
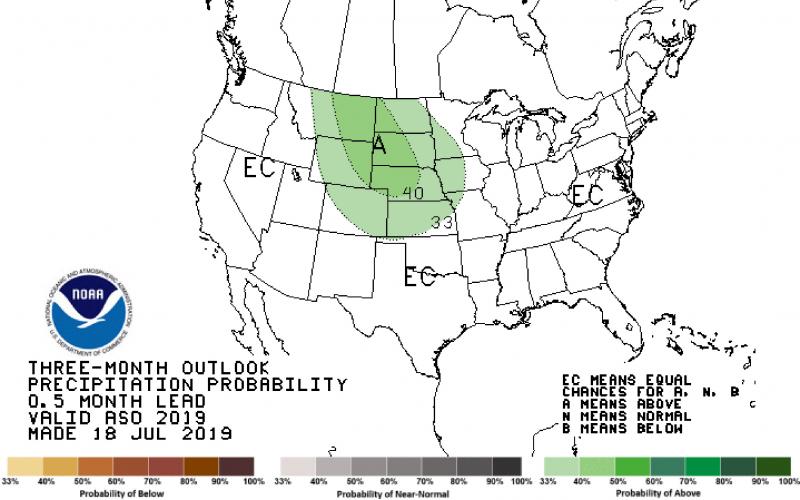
Wet Conditions Likely Into Fall Season
Many locations in South Dakota have already received as much precipitation this year as they do in an entire average year. The latest climate outlook from NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center shows increased chances of wetter than average conditions to continue into the fall season.
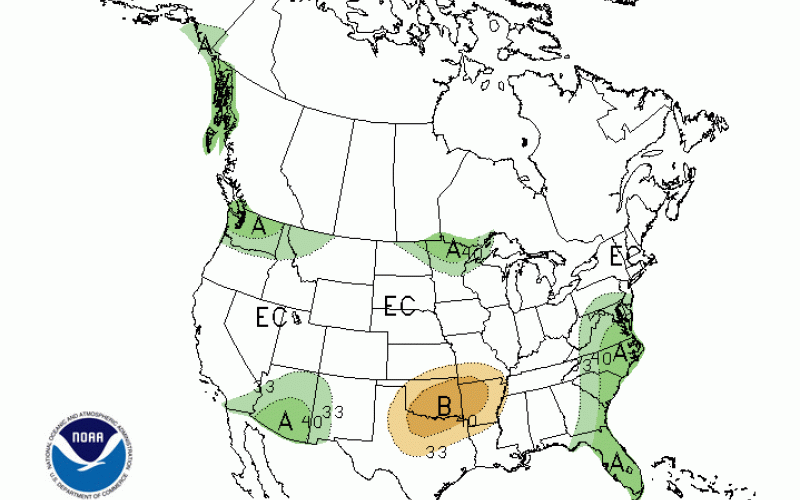
Fall Frost and September Climate Outlook for 2019
September 2019 has been pleasantly warmer than usual, and our crops need every bit of that warmth to reach maturity before our first frost arrives. Fortunately, temperatures have cooled slightly this week but just to near average for this time of year.
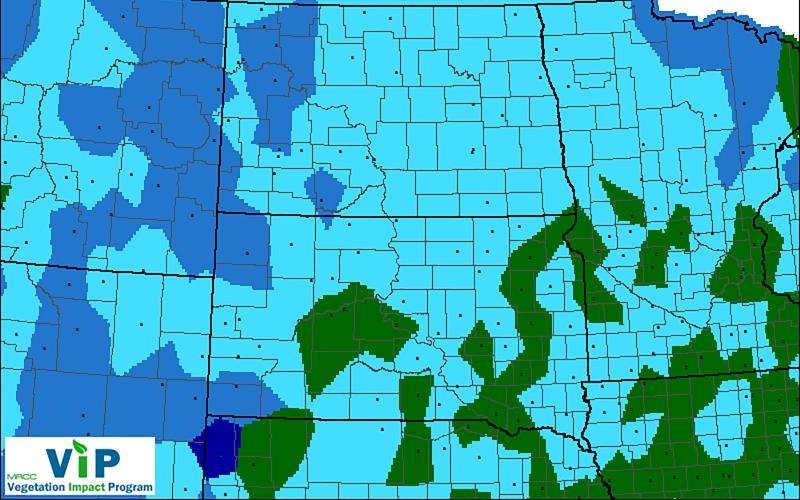
Fall Frost and September Climate Outlook for 2019
This year’s struggles with weather and climate are continuing this fall. Late planting of corn and soybeans in the spring have now combined with near average or cooler than average summertime temperatures. This combination has led to slow crop growth and the need for an extended frost-free season to ensure these crops reach maturity.
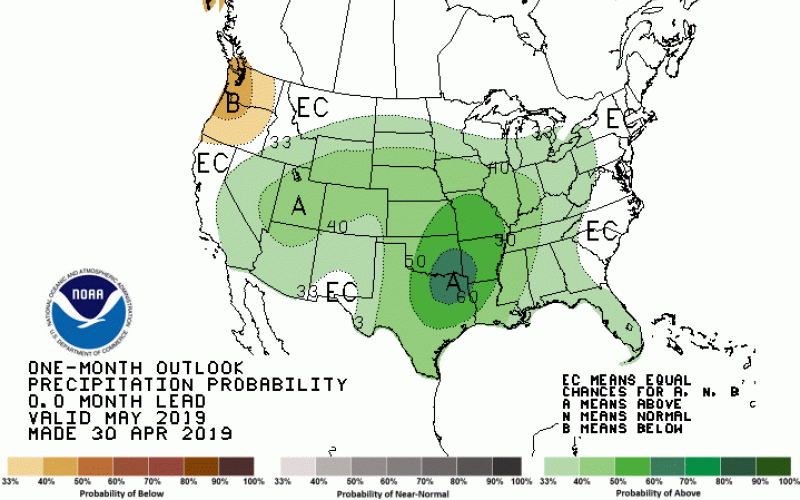
May 2019 Climate Outlook: April Showers Bring May Showers?
The precipitation outlook for May does not show much promise of relief from moisture, as wetter than average conditions are slightly more favored than drier conditions. In addition, cooler than average temperatures are more likely for the first half of May and could continue for much of the month.
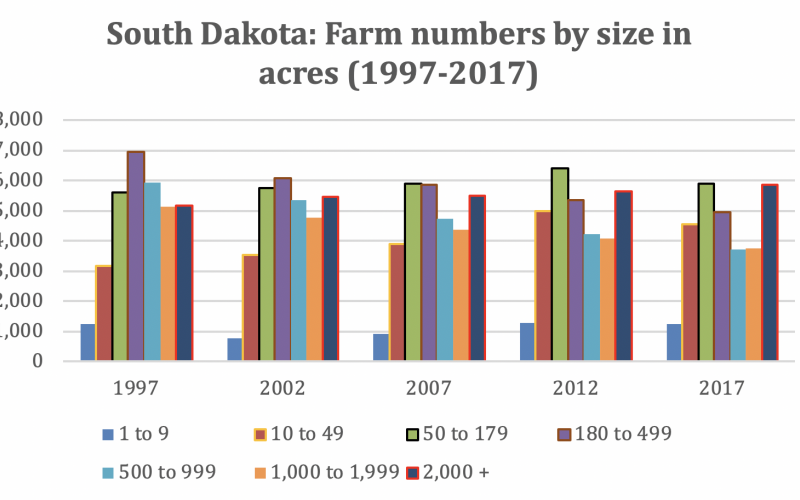
Farm Size in South Dakota: Where Are We Heading?
Agriculture is going through some difficult times not only in the United States, but globally as well. Aside from some short-lived price hikes for different products, the overall trend has been to higher costs of production and lower output prices.
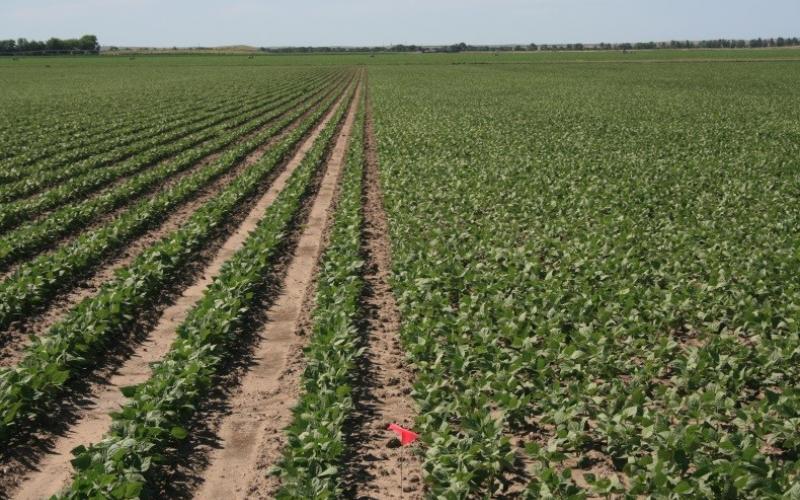

Field Studies: Replicated Comparisons vs. Side-by-Side Comparisons
How should a basic study be set up or laid out in the field? One very common approach is to divide a field in half and compare the halves or possibly compare two fields in close proximity and see which variety or practice yields highest. This approach can end with very misleading results because of the variability that exists across a field or fields due to many factors.

Field Studies: What do You Mean 5 Bushels Per Acre is Not Significant?
Utilizing sound research results to help make decisions on the farm is a wise business practice. It can be confusing, however, when you see two numbers that are clearly not the same labeled as “not significantly different.”
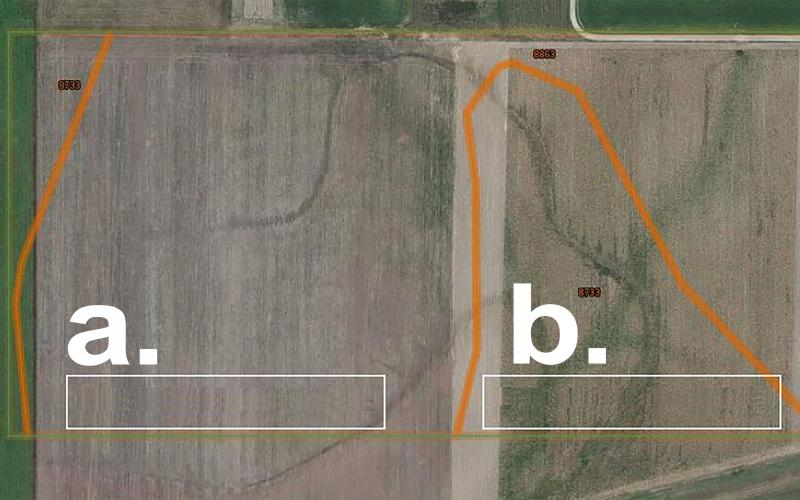
Field Studies: Setting up a Trial
Increasingly, farmers are generating on-farm research data that encompasses a wide-range of practical topics. However, setting up those experiments so that the data is statistically valid is not necessarily common knowledge.
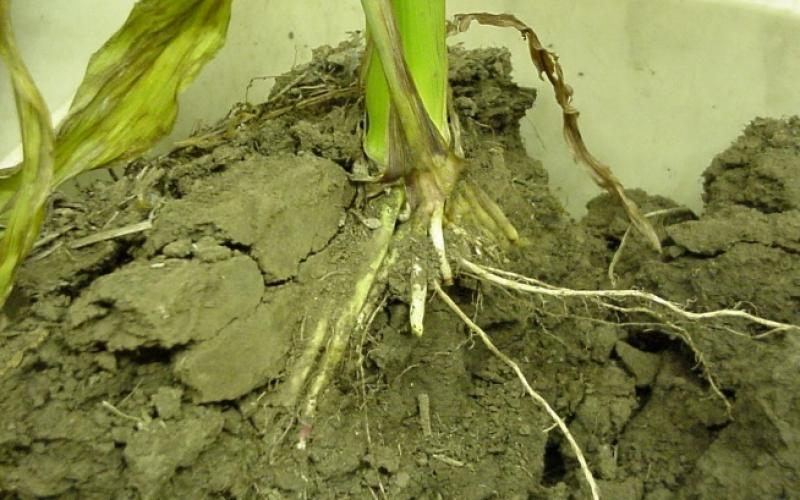

Planting Into Wet Soils
It is evident that there are high chances of planting into wet soils this spring. This is not a good decision when normal soil conditions appear to be attainable, but this year we may not have a choice.
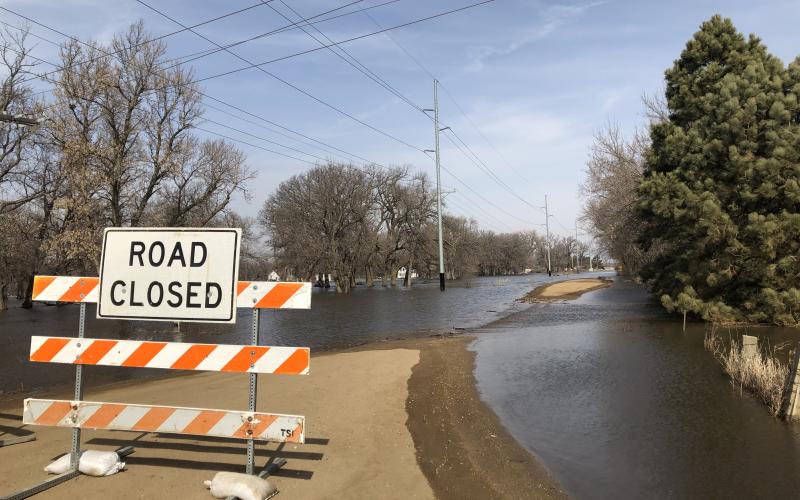

Floods Continue With a Wet Outlook
As April unfolds, major flooding continues along the Eastern rivers. The James River is at crest in Brown county the first week of April and will slowly recede while maintaining flood level for much of April.