About Liver Abscesses
The toughest losses to control are often the ones we cannot see. Liver abscesses are a great example of an important value robber in feedlot cattle that’s not immediately apparent. Even though we can’t tell by looking if cattle have liver abscesses, the problem is certainly visible at the packing plant and in lost profit opportunities.
Profit Impact
In addition to the most obvious losses (condemned livers, resulting in about $10 to $16 per head lost export value) other profit robbers can include:
- Poorer feedlot performance and efficiency.
- Reduced carcass weights and increased trimming losses.
- Reduced output and capacity at the packing plant.
Causes
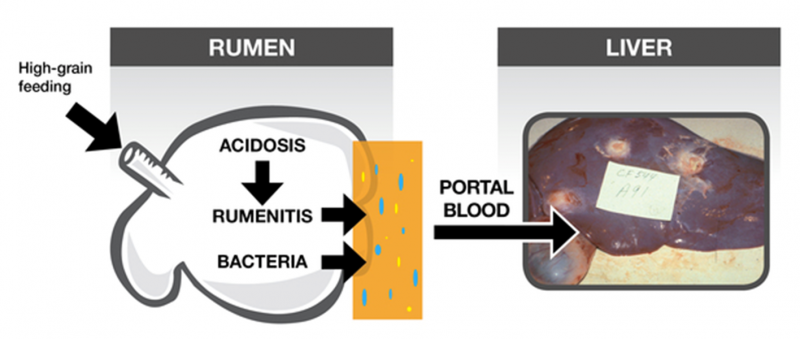
Liver abscesses are caused by the same pathogenic bacteria responsible for footrot (Fusobacterium necrophorum and Trueperella pyogenes). A key contributing factor to the development of liver abscesses is damage to the cells lining the rumen wall due to excessive acid load or other physical irritants. The irritation allows for these pathogens to pass from the rumen to the portal blood and eventually to the liver (Figure 1).
Incidence rates in beef cattle average roughly 15% with some variation depending on sex and geographical region. Recently there has been a marked increase in the level of liver abscesses in Holstein steers with infection rates increasing from 12% in 2003 to as much as 55% in 2013. This could be related to the fact that dairy steers are typically fed a high concentrate diet for a longer period of time compared to beef breeds.
Treatment
Feeding antibiotics is the most common method of controlling liver abscesses in feedlot cattle in the U.S. The most commonly used product today is tylosin. Research shows that tylosin is effective in reducing the incidence of liver abscesses by about 40 to 70% compared to untreated cattle. Keep in mind that feeding tylosin does require a Veterinary Feed Directive in order to be used in feedlot diets.
The combination of VFD requirements as well as increased scrutiny of antibiotic usage in livestock diets in general has led to increased interest in control measures that do not rely on antimicrobials. Strategies such as feeding essential oils and vaccinating against F. necrophorum have been studied, but unfortunately these approaches have not been consistently effective. This will be an active area of research now and in the future to increase the options available to control liver abscesses.
Management Considerations
As with most diseases and production issues, management plays a critical role in reducing the incidence and negative impact of liver abscesses. As mentioned earlier, acidosis and increased risk of liver abscesses usually go hand in hand. Management practices that reduced the risks of acidosis and other metabolic disorders include:
- Avoid stepping up cattle to high starch diets too rapidly.
- Minimize daily feed intake variation.
- Make sure there is adequate effective fiber in the diet. Finely ground roughage does not promote sufficient rumination and saliva production to help buffer rumen pH.


