Diseases & Disorders
All Diseases & Disorders Content
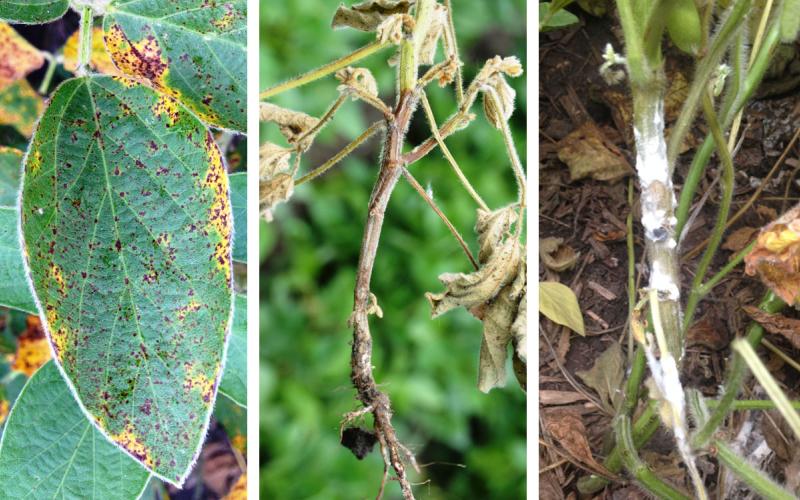

Mid-to-Late Soybean Disease Management
Even though it has been hot and humid this summer, some soybeans around the state have seen ideal conditions for mid-to-late season disease development. Learn some common diseases to scout for.

Are Fungicides Needed on Crops Damaged by Wind, Sand Blasting or Hail?
When extreme weather brings hail and sand blasting to fields, many growers wonder if a fungicide application is needed afterwards to protect wounded plants from bacterial diseases.
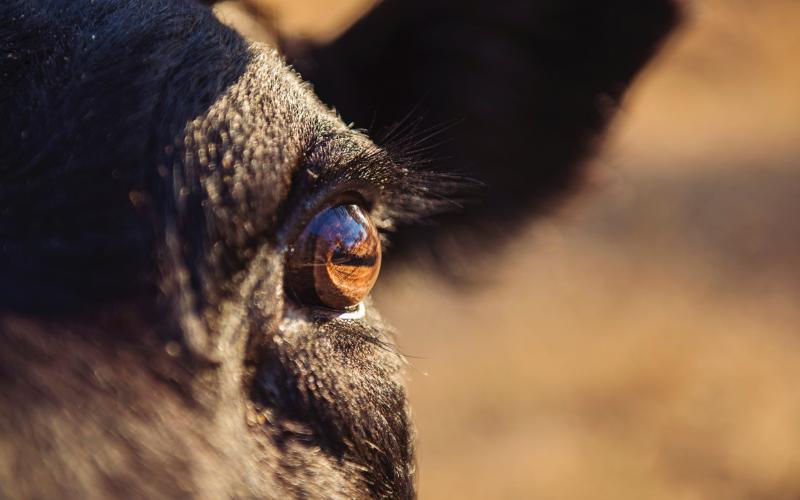

Veterinarians Remind South Dakota Cattle Producers To Include Anthrax Vaccination This Spring
May 23, 2022
SDSU Extension and South Dakota Animal Industry Board veterinarians are encouraging South Dakota cattle producers to include the anthrax vaccine in their vaccination program when they turn out cattle to summer pastures this spring.

The Connection Between Diet and Acne
Acne vulgaris is one of the top skin conditions in the United States, impacting around 40 to 50 million people. Attention around the connection between diet and acne has been the focus of new research, specifically around high-glycemic diets.
Aphanomyces Root Rot of Alfalfa
Fact sheet on Aphanomyces Root Rot of Alfalfa

Best Management Practices for Sunflower Production
This is your unbiased, research-based guide to sunflower production, providing the latest recommendations to help increase yield, reduce input costs and protect your investment.
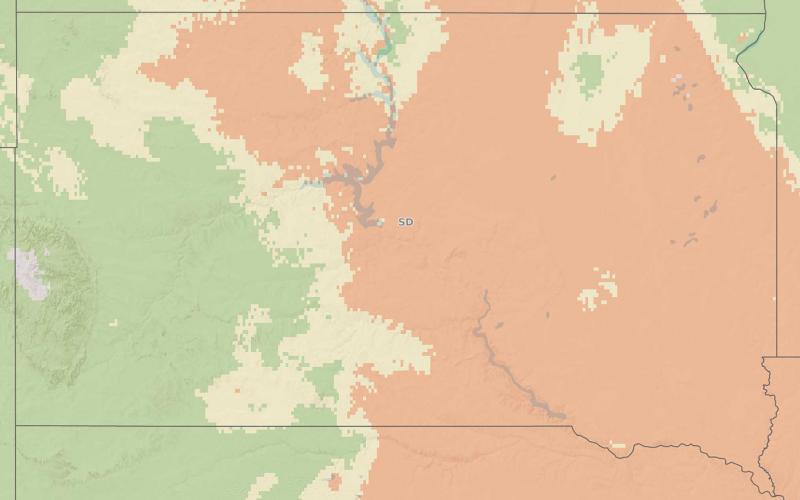
The Fusarium Head Blight Prediction Tool
The Fusarium head blight prediction tool, available through Penn State University and Mesonet at SDState, uses weather variables to predict the risk for Fusarium head blight in wheat.

Pre-Plant Wheat Streak Mosaic Disease Management Strategies
Drought conditions tend to promote high wheat curl mite populations. Wheat streak mosaic virus and other viruses transmitted by wheat curl mites are best managed through cultural practices performed before planting.

Wheat Streak Mosaic of Wheat
Fact sheet about symptoms, disease cycle, risk factors and management of Wheat streak mosaic disease

Scout for Corn Ear Rots
Several corn fields scouted in northeastern South Dakota counties were found with ear rots. Ear rots were mostly prevalent in areas that experienced hailstorms in the recent past. Ear rots in corn are caused by a few fungal pathogens, and which ear rot develops depends on the weather conditions.