Soybean Insects
Recommended Content

Best Management Practices for Soybean Production
This is your unbiased, research-based guide to soybean production to help increase yield, reduce input costs and protect your investment.
All Soybean Insects Content
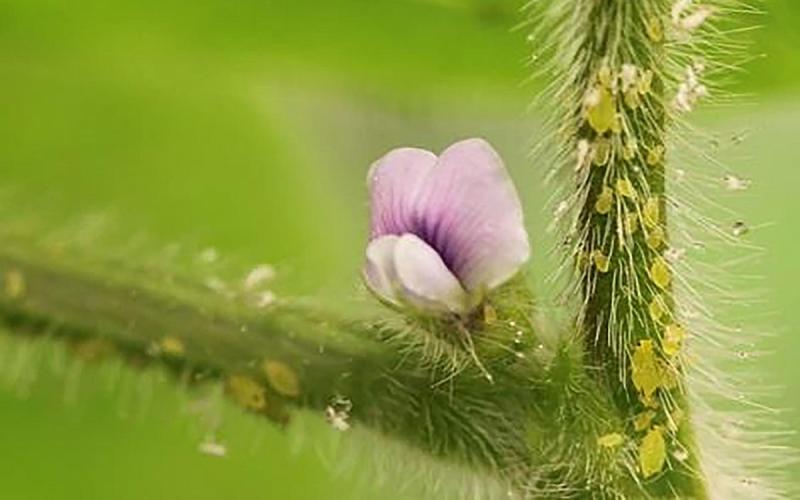

Soybean Aphids Active in South Dakota
Soybean aphid populations have been observed in South Dakota. Although populations are still very small and not widely dispersed, it is a good reminder that soybean aphid scouting should occur throughout the growing season.
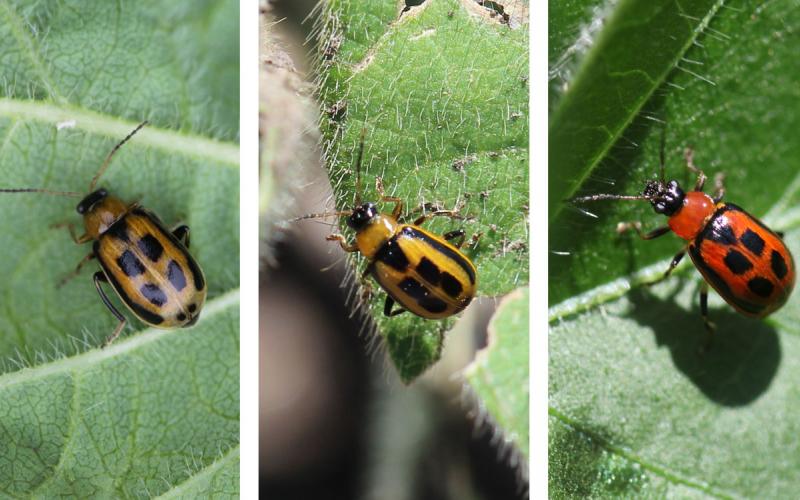

Monitor Soybean for Bean Leaf Beetle Activity
Some of the bean leaf beetles we are currently observing in South Dakota may make up the population of overwintering adults. While these adults are in soybean, they can cause significant amounts of defoliation to the leaves.
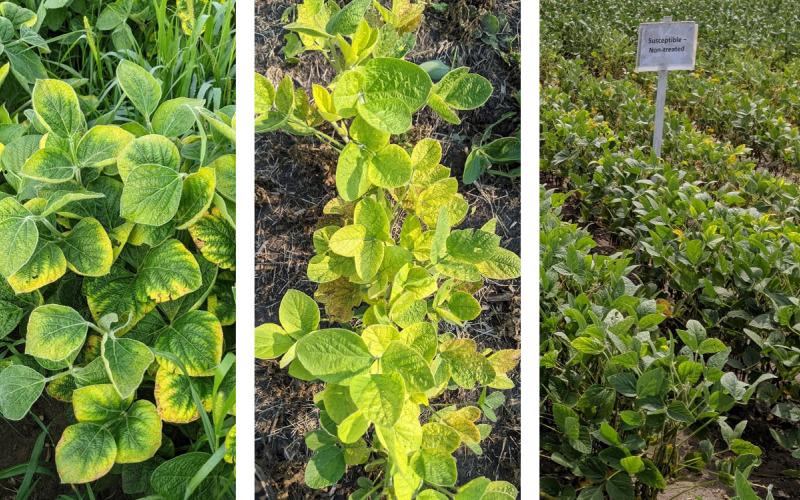

What Is Causing Soybeans to Yellow at This Time?
Recently scouted soybean fields were observed with yellowing plants, and one field was found to have plants dying prematurely. Learn some of the factors that may cause soybean plants to yellow at this time in the growing season.
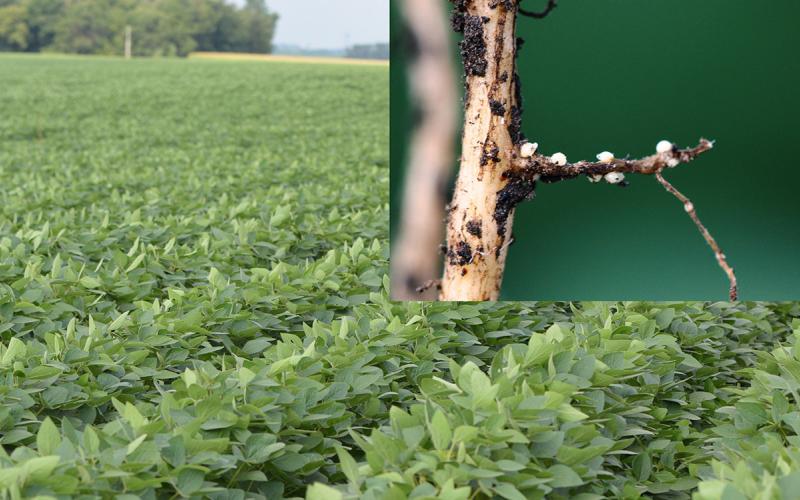

Drought Conditions May Increase Soybean Cyst Nematode Population in Soil
Moisture stress coupled with above-normal temperatures have been linked with increased soybean cyst nematode populations in the soil. In order to keep populations in the soil below the yield-reducing levels, there are a few management practices which can be used.
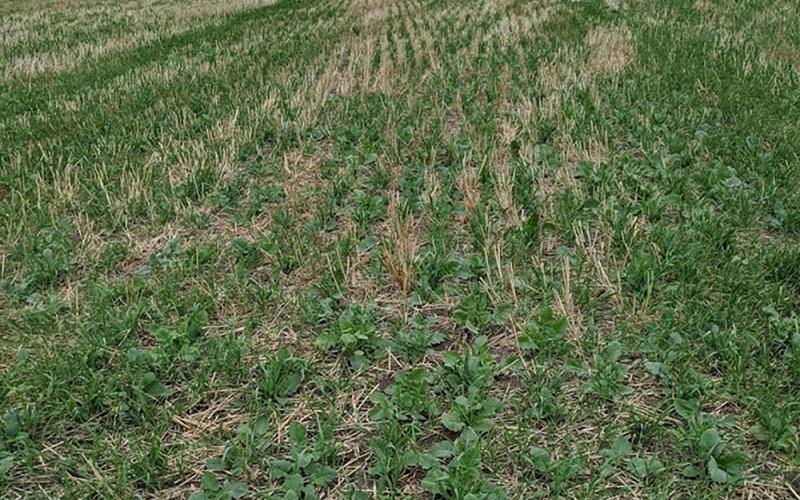

Cover Crop Considerations When Dealing With Soybean Cyst Nematode
With the soybeans being harvested a little earlier than usual this year, some producers are finding themselves making management decisions that include cover crops. For soybean producers dealing with soybean cyst nematode in their fields, selection of cover crops is important since some of these can be hosts for soybean cyst nematode.

Soybean Cyst Nematode Management Plans Should Include Proactive Weed Management
While soybean cyst nematode can be managed through use of resistant varieties and crop rotation, presence of alternative weed hosts can negate the benefits of these practices by providing a host for soybean cyst nematode to continue to accumulate in the soil.
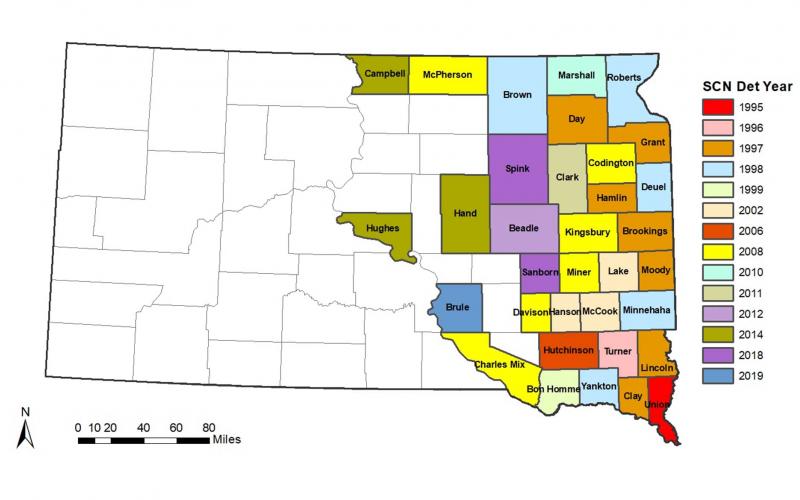
HG Type Testing: A Management Strategy for Soybean Cyst Nematode Control
Have you noticed lower soybean yielding areas in your field? Soybean cyst nematode may be to blame. Fall, and especially after soybean harvest, is the best time to sample soil and have it tested for soybean cyst nematode.
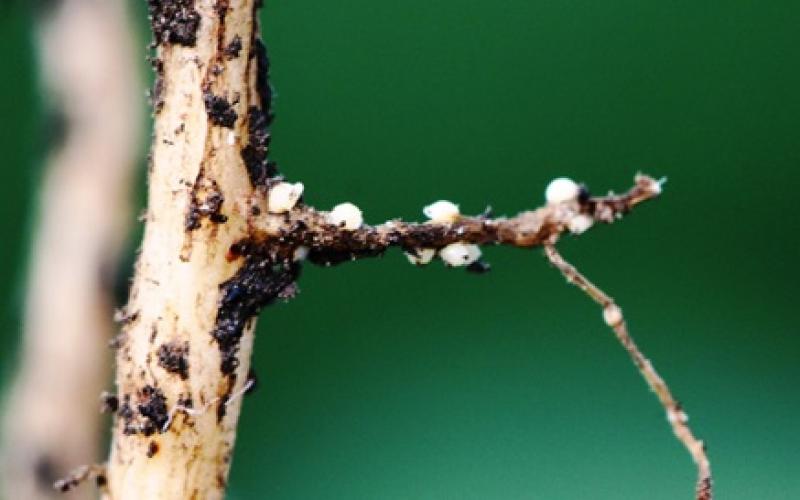

Soybean Cyst Nematode in South Dakota: History, Biology, and Management
Factsheet about Soybean Cyst Nematode history, biology and management in South Dakota
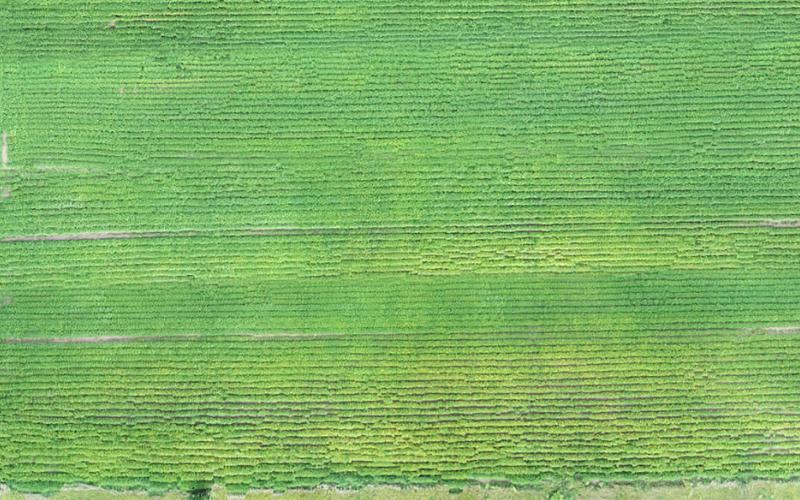

Early Yellowing in a Soybean Field May Indicate Presence of the Soybean Cyst Nematode
Some portions of soybean fields may show clusters of plants yellowing while the rest of the field is still green. One of the factors that could lead to soybean plants showing early yellowing in clusters is soybean cyst nematode (SCN).

Pre-Plant Disease Management Considerations
If the forecast holds true, it looks like it is going to be another year of excessive soil moisture and possible flooding come this spring. The increased level of soil moisture has implications with regards to plant stand establishment as well as root rot and nematode infestations.