Search
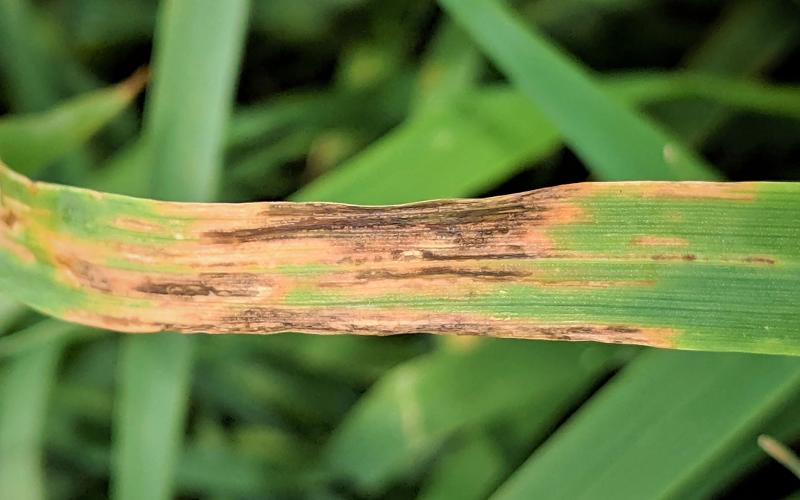

Bacterial Blight Developing in Oats
Oats scouted in a few fields in the Eastern and South Central parts of the state were found with bacterial blight developing on the lower leaves. Plants infected have leaves with water-soaked brown longitudinal lesions in the top-half of the leaf. Severe symptoms can lead to premature leaf death.
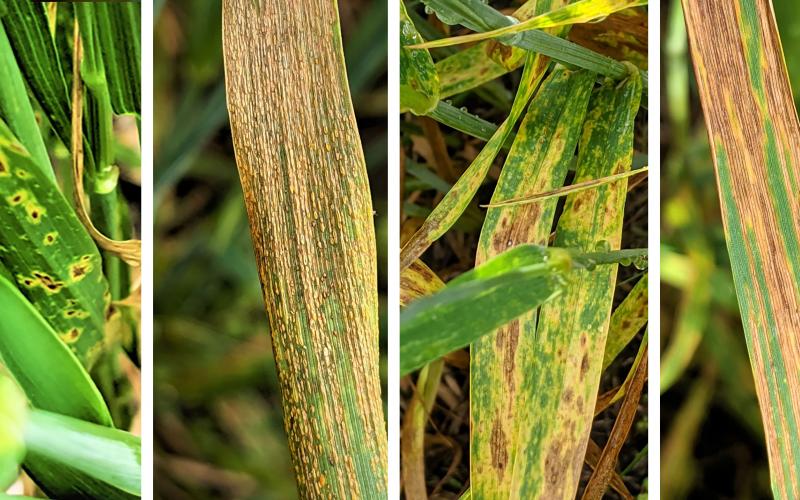

Winter Wheat Disease Update: Leaf Diseases and FHB on the Increase
Winter wheat fields scouted last week show an increase in fungal leaf diseases and bacterial leaf streak. Among the fungal diseases, the most common leaf diseases are tan spot, Stagonospora leaf blotch, and stripe rust. The risk for Fusarium head blight has also started to increase in a number of areas in the state.

Buying or Selling Oats for a Cover Crop? Be Sure to Follow the Rules
As a challenging 2019 row crop planting season wraps up in South Dakota, many producers are looking to plant cover crops on unplanted acres. One popular cool-season grass cover crop is oats. Most oats in South Dakota are grown as certified varieties, and it is important to be aware of the legal ramifications behind purchasing oat seed for use as a cover crop.
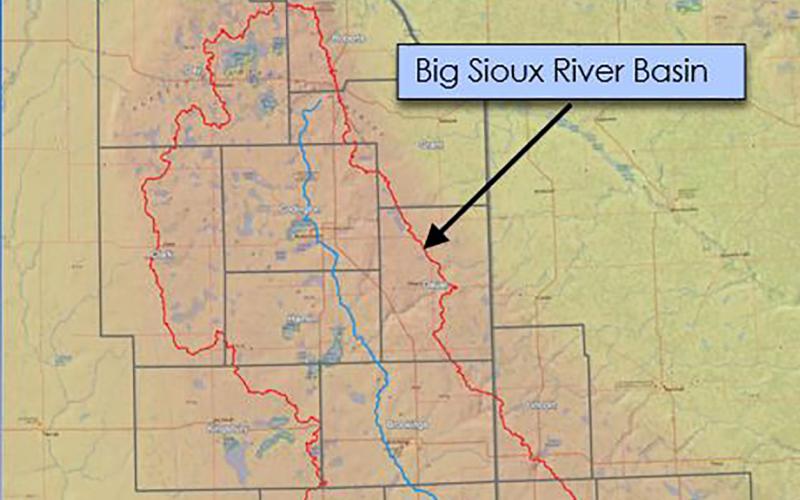
Big Sioux River Flood Information System Sees Heavy Use During Spring 2019
The Big Sioux River Flood Information System is the result of a combined effort between the SD Department of Environment and Natural Resources, local governments, and private industry, to create a product that can be used to predict the impact of flood events in the Big Sioux River Basin.

Cover Crops 2019: What to Plant When
As many Midwest producers look to cover crops to build soil health and provide supplemental forage after a soggy spring, many questions are arising regarding management decisions, specifically, species selection and planting timing.
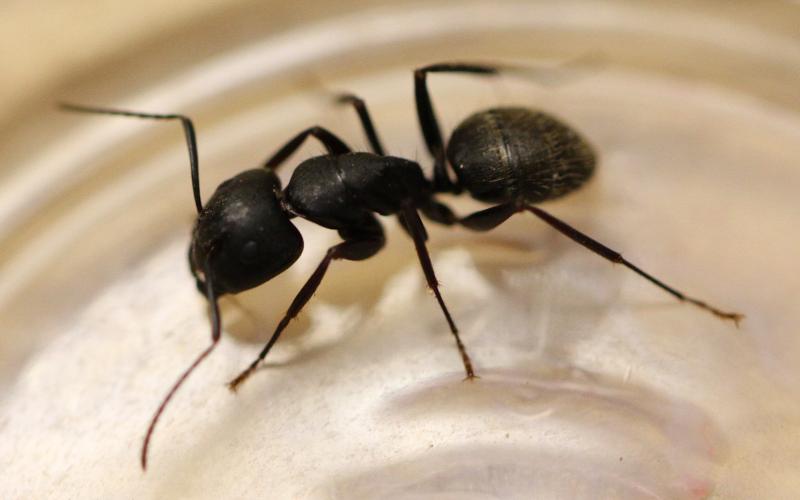

Watch Out For Carpenter Ants
With the continued moisture and warmer temperatures, carpenter ants have become a more common appearance in South Dakota. Similar to termites, this insect can be a structural pest, causing damage to homes and other buildings. It is important to identify and treat carpenter ants early to prevent any potential damage.
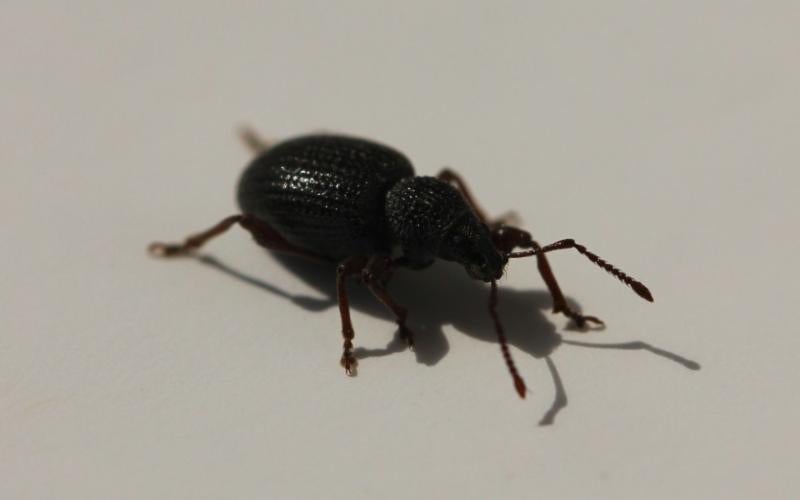

Black Vine Weevils Becoming Active
Black vine weevils are now showing up across the state. It is typical for the adult beetles to emerge in early summer and begin feeding on plant foliage. They primarily feed on lilacs and yews, both common landscape shrubs. Although the adults cause minimal damage, their larvae feed on the roots and can occasionally be a threat to ornamental plants, especially those grown in pots or containers.

Monitor Canola Fields for False Chinch Bug Activity
While scouting canola this week, I came across a field that had plants along the edge that looked like they were suffering from drought stress, but given the recent rain I doubted that to be the case. Closer inspection of the stressed plants indicated that they were covered in false chinch bugs. Although false chinch bugs are not normally an issue in canola, very large populations do have the potential to reduce yield.
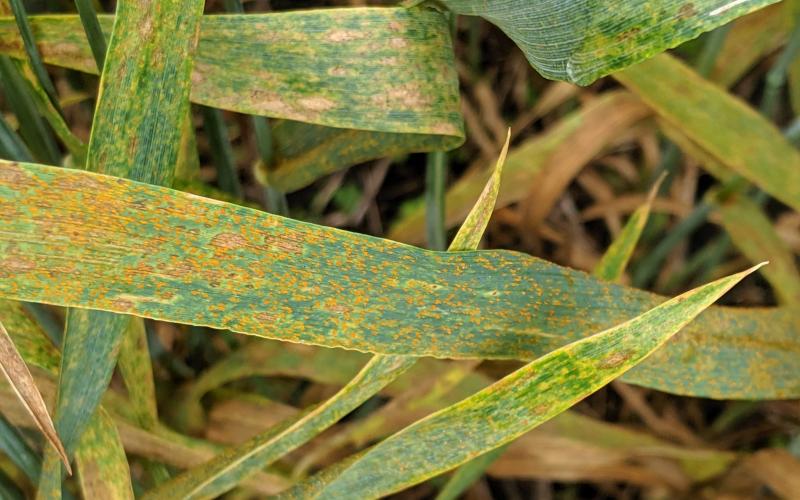

Diseases in Winter Wheat Imply High Inoculum for Spring Wheat
Winter wheat is past the need for an in-season fungicide application. However, many spring wheat fields are yet to flower, making them prone to disease development. A few diseases, including leaf rust, stripe rust, and Fusarium head blight have developed in winter wheat. This implies that there is enough inoculum available for these diseases to develop in spring wheat; especially East River, where rainfall has been frequent.
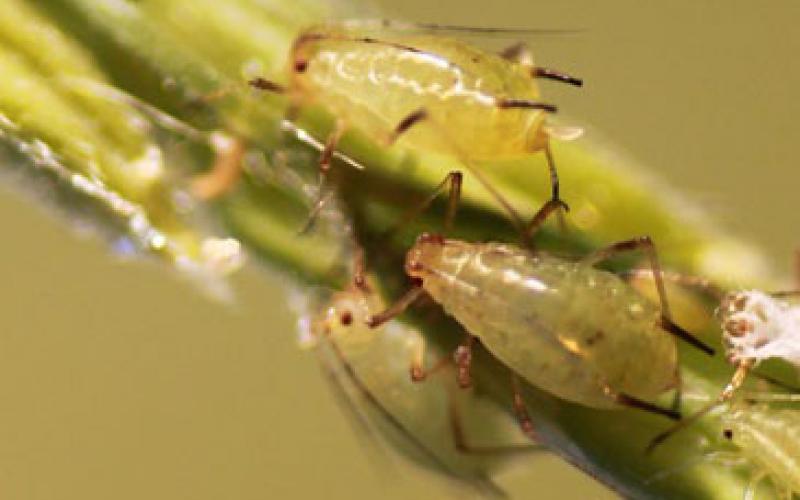

Continue Scouting Wheat for Aphid Populations
Aphid populations in winter wheat continue to be observed in South Dakota. The major questions now are whether or not aphid populations are at economic threshold and if spraying is really necessary.