Written by Claudia Botzet, former SDSU Extension Nutrition Field Specialist.
The Nutrition Facts Panel, often referred to as the food label, is a great tool to help us learn more about the ingredients and nutritional value included in a food product. This, in turn, can help us be better informed when making food-related decisions when buying groceries and dining out. The food label breaks down the nutritional value found in the food by including the calories, carbohydrates, fat, fiber, protein and vitamins per serving.
Let’s take a look at what you will find on the food label.
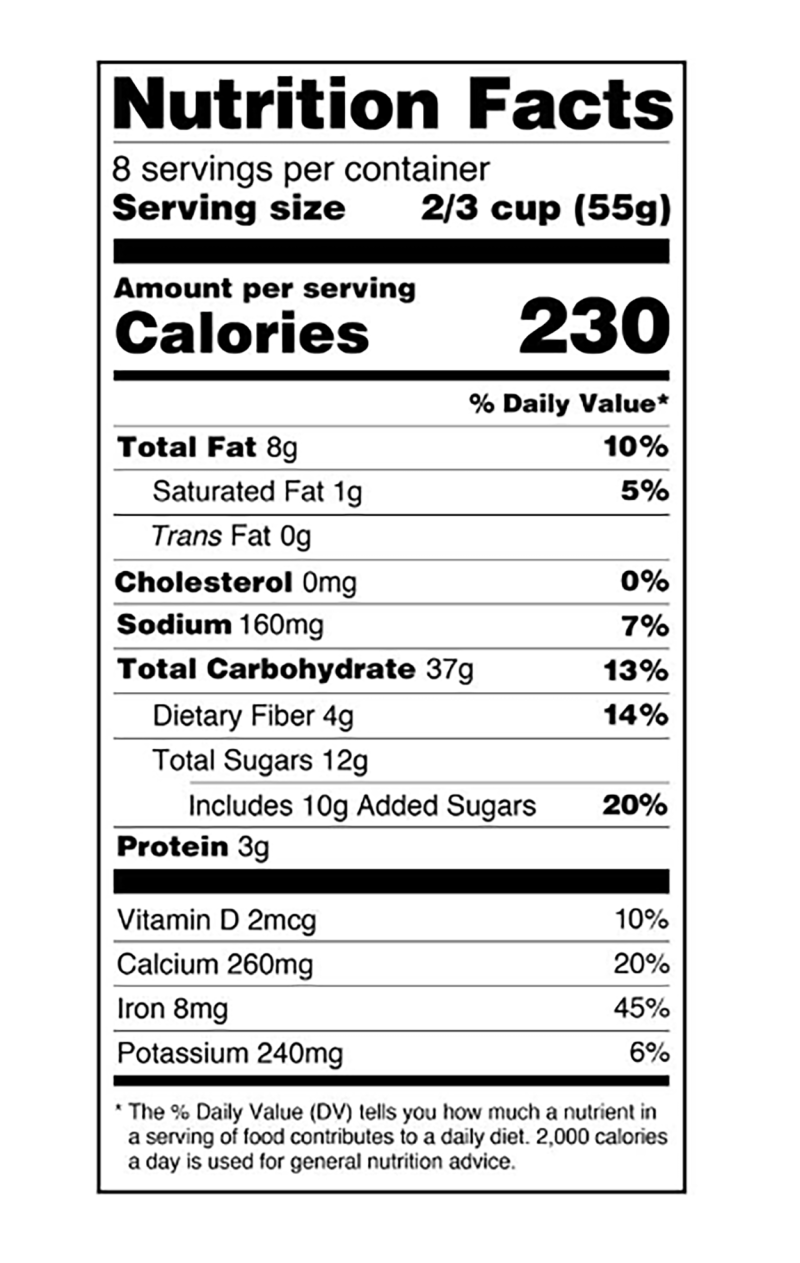
Serving Size
- First, find the Serving Size. This shows the amount per serving and the number of servings in the package.
- You can use this information to determine the nutrition of the portion size you chose to eat. Looking at the serving size can also help you to compare the nutrition of similar products.
Total Calories
- Next, compare your individual needs to the Total Calories. The calorie number shown is for one serving of the product. Look at how many calories are in one serving and compare it to your individual needs.
- General nutrition recommendations are based off 2,000 calories per day, but your individual needs may be higher or lower depending on age, height, weight, sex, and physical activity level.
Percent Daily Values
- Use the Percent Daily Values as a guide. The Percent Daily Values (DV) tell you how much one serving contributes to your daily intake.
- For example, a food product with a 15% DV of carbohydrates provides 15% of total daily carbohydrate intake for a person who needs 2,000 calories per day. Your calorie needs may be different, so you may need more or less than 100% of the DV that is listed on a product for certain nutrients.
- A low DV would be 5% or less. Look for DVs low in cholesterol, saturated fat, and sodium.
- A high DV would be 20% or greater. Look for high DVs in dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
Saturated Fat, Added Sugars, and Sodium.
- Moderate your intake of Saturated Fat, Added Sugars, and Sodium. Consuming less saturated fat, added sugars, and sodium may help lower your risk for developing a chronic disease.
- The Dietary Guidelines for Americans (DGAs) recommend less than 10% of calories per day should come from saturated fat and added sugars.
- The DGAs recommend consuming less than 2,300 milligrams (1 teaspoon) of sodium per day.
Dietary Fiber, Vitamins, and Minerals
- Don’t be shy when it comes to Dietary Fiber, Vitamins, and Minerals. Fruits and vegetables are great sources of dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
- Choosing foods that have calcium, dietary fiber, iron, potassium, and Vitamin D may help lower your risk of developing a chronic disease.
Protein, Carbohydrates, and Fat
- Lastly, you can look for Protein, Carbohydrates, and Fat.
- The DGAs recommend that 10 to 35% of your daily intake be protein.
- When choosing a protein source, look for lean meats, poultry, fish, dairy products, beans, nuts, and seeds.
- The DGAs recommend 45 to 65% of your daily intake be carbohydrates.
- When choosing carbohydrate sources, look for whole grains, refined grains, fruits, and certain vegetables.
- The DGAs recommend 20 to 35% of your daily intake be fat.
- Although the Nutrition Facts Label does not always include this information, look for monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, and consume less saturated fat.
Nutrition Terms

- Low calorie: 40 calories or less per serving.
- Low cholesterol: 20 milligrams or less and 2 grams or less of saturated fat per serving.
- Reduced: At least 25% less of the specified nutrient or calories than the usual product.
- Good source of: Provides at least 10 to 19% or more of the DV of a vitamin or nutrient per serving.
- Excellent source of: Provides at least 20% or more of the DV of a vitamin or nutrient per serving.
- Calorie free: Less then 5 calories per serving.
- Fat free/sugar free: Less than ½ gram of fat or sugar per serving.
- Low sodium: 140 milligrams or less of sodium per serving.
- High in: Provides 20% or more of the DV of a nutrient per serving.
What about the Ingredient List?
The ingredient list tells you what ingredients are in the product. The ingredients are listed by the greatest amount first, followed by descending order of ingredients in smaller amounts.
The ingredients list is a great reference when comparing similar foods from different brands, or when looking to exclude specific ingredients from your diet due to a food allergies for example. If the product has a major food allergen in it, they will be listed in bold at the end of the ingredient list. The major food allergens are milk, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, and soy.
The Nutrition Facts Label can be intimidating at first glance, but once you are able to break it down and understand it, reading the label can become a breeze. The information on the food label can help us make health-conscious food choices to live a happier and healthy life.
References
- U.S. Department of Agriculture and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025. 9th Edition. December 2020.
- Sarah Klemm. The Basics of the Nutrition Fats Label. Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. March 4, 2022.
- Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. New Nutrition Facts Label.


