Natural Resources
All Natural Resources Content

SDSU Extension Releases Guide for Landowners Involved in Wind or Energy Development
September 18, 2020
Recent energy development projects have impacted several regions of South Dakota with disturbance to native soils.

Soil Testing for Vineyards in South Dakota
Not all soils are conducive to growing quality grapes, so prospective vineyard sites should be tested before a decision is made to plant grapes. Tests can identify soils that are either too high in pH, salts, or salinity, or that are “too rich” (too high in organic matter and nitrogen) for grapes. In addition, testing before planting allows for the incorporation of nutrients—such as phosphorus—that do not move easily through the soil to plant roots.

Junior Arborist Activity Guide
The Junior Arborist Activity Guide provides objectives, content, equipment and supplies needed to complete 8 modules of arboriculture instruction, helping schools and other educational programs to create a youth arboriculture program of their own.
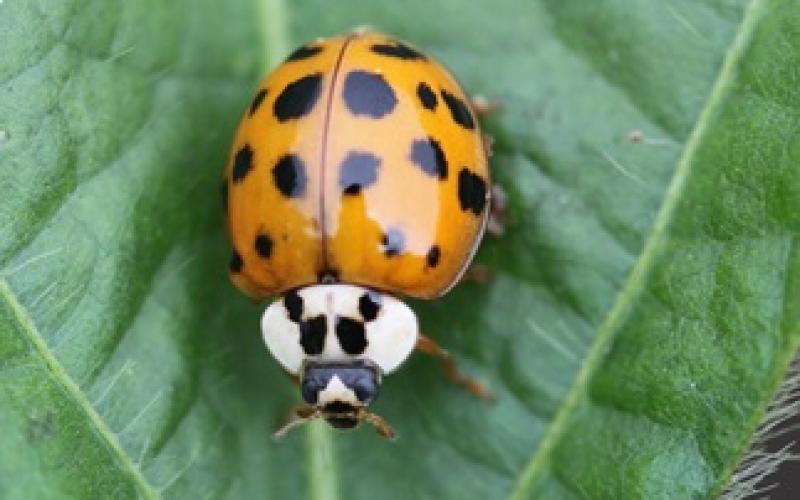

Lady Beetles of South Dakota
A guide for monitoring, properly identify, and promoting the growth of lady beetles.

Understanding Contract Language and Restoring Native Grassland Damage after Energy Development
Energy development on private lands can result in locally heavy land manipulation. Of particular concern is the manipulation of native grasslands and other sensitive areas and how it will affect those areas in the short-and-long-term.
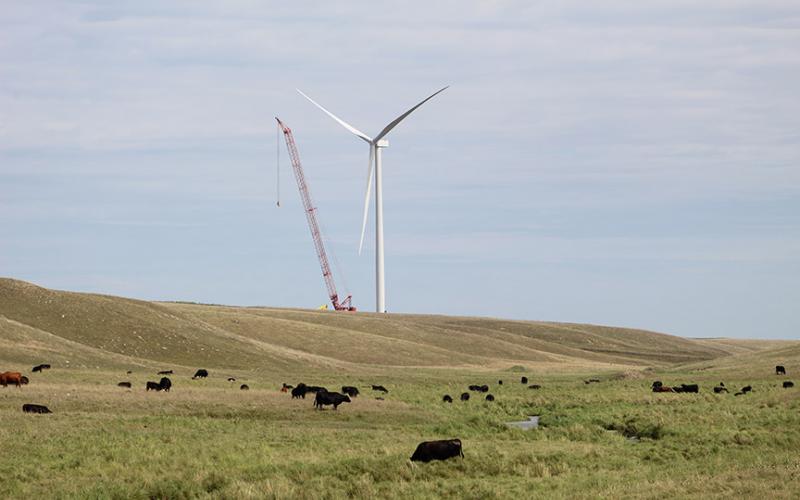

Best Management Practices Guide for Restoration of Native Grasslands and Sensitive Sites Resulting from Energy or Industrial Development
A general guide to South Dakota landowners who are considering or who have allowed energy or other industrial development on their property.
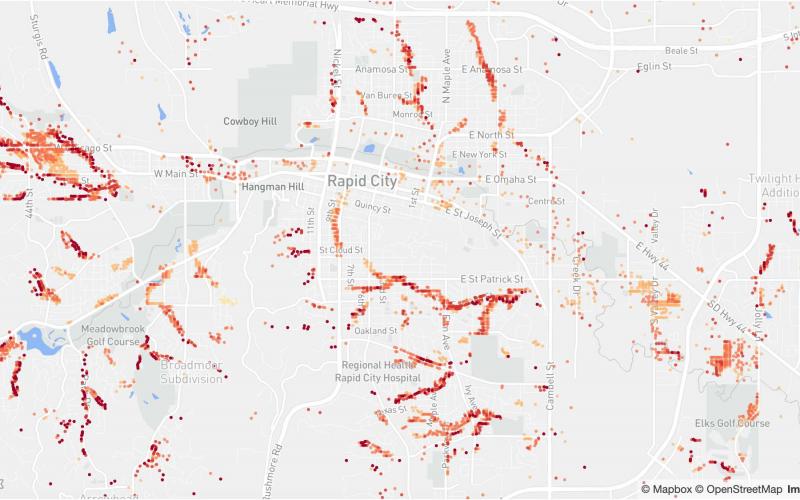
South Dakota’s Changing Flood Risk
South Dakota’s flood risk is increasing in some areas of the state according to a recent report from the First Street Foundation. In 2020, 62,600 total properties are at substantial risk, with a projected increase to 63,000 properties by 2050.
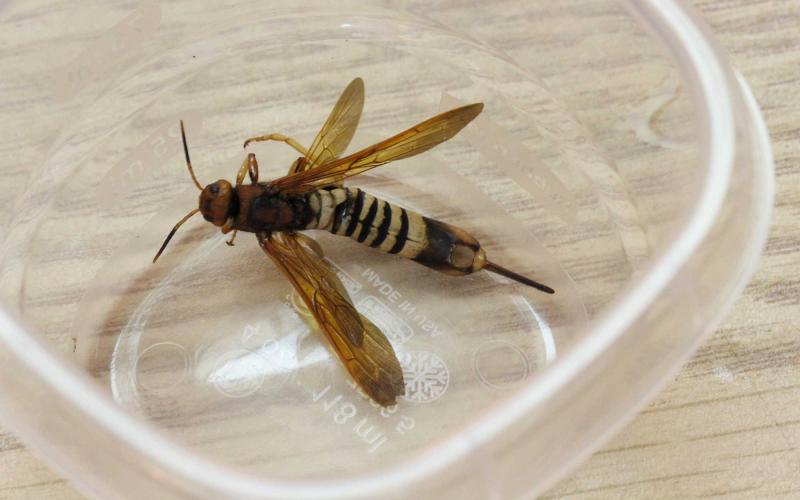

Huge Wasps on My Tree! No, Those Still Aren’t Murder Hornets.
Another insect that has been mistaken for the Asian giant hornet (also known by its media-popularized name of ‘murder hornet’) is the horntail wasp. Horntail wasps are wood-boring insects that are harmless to humans, as they do not have venom and cannot sting.
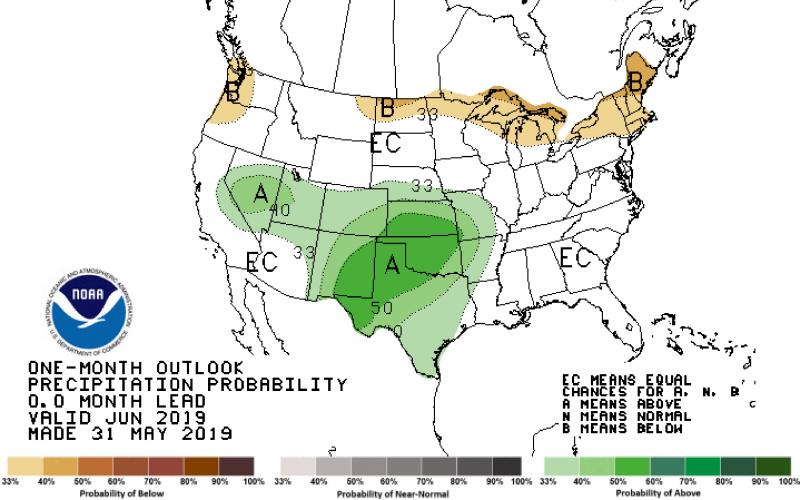
June 2019 Climate Outlook for South Dakota
As South Dakota emerges from the wettest 12-month period in 124 years of climate recordkeeping (June 2018-May 2019), June has started warmer and drier than average. The outlook, however, turns towards cooler and wetter than average again for the middle of the month.
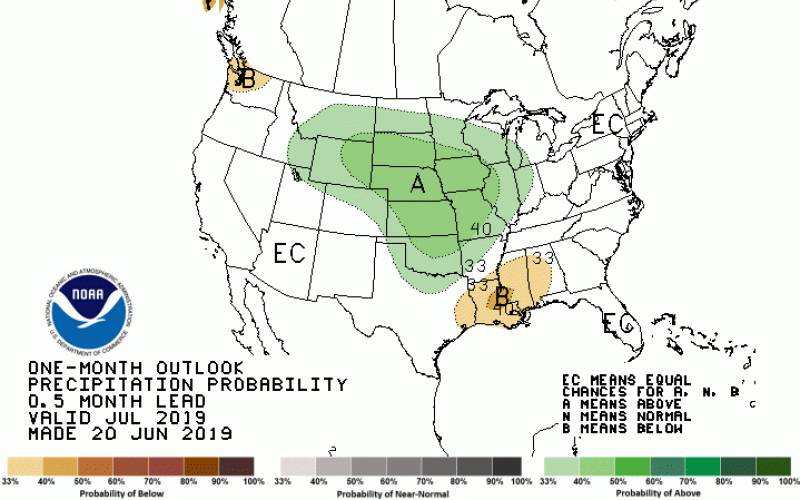
July 2019 Climate Outlook: Challenges Continue
This year’s seasonal pattern of wetter than average conditions is projected to continue through July and the rest of the summer season. The latest climate outlook, released June 20, 2019, shows an increased chance of wetter than average conditions in the next one to three months for the state of South Dakota.