Written collaboratively by Adam Varenhorst, Philip Rozeboom, Patrick Wagner, and Brad McManus.
Article Originally Submitted: May 17, 2024
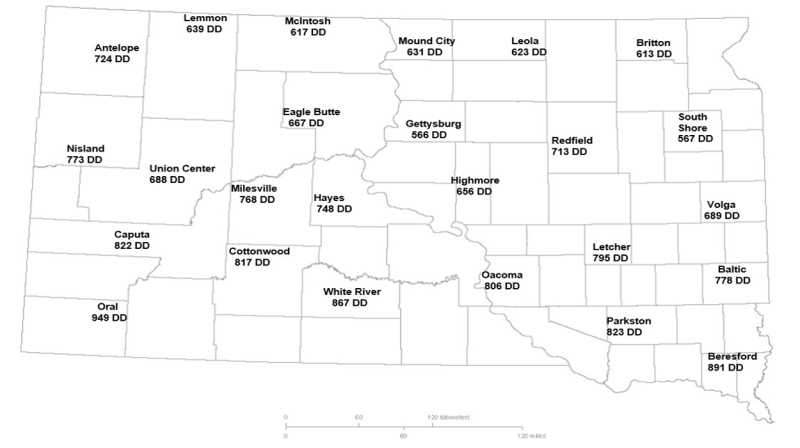
Although degree days are accumulating, the highest value in South Dakota for common stalk borer is 949 degree days after this week. Based on this, no scouting is necessary for common stalk borer activity at this time.
Common stalk borer caterpillars are still active in grass and weeds along field edges. It’s important to remember that spraying these plants with herbicides at this time could cause a premature emergence of the common stalk borer and an increased infestation of corn that is adjacent to the edges.
Predicting Common Stalk Borer Migration Into Corn Fields With Degree Days
The hatching and movement of common stalk borer caterpillars can be estimated by using degree days with a developmental threshold of 41 degrees Fahrenheit. Common stalk borer eggs typically begin to hatch at 575 degree days. The caterpillars finish hatching and begin development on weeds and grasses at 750 degree days. At 1,300 degree days, 10% of the caterpillars will begin moving to corn. Corn should begin to be scouted at this point. At 1,400 degree days, 50% of the caterpillars will or have moved into corn.
As a reminder, the equation for degree days is:
(Maximum Daily Temperature + Minimum Daily Temperature) ÷ 2 - The Developmental Threshold
| Accumulated Degree Days |
Common Stalk Borer Caterpillar Activity |
Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| 0-574 | Conditions favorable for egg hatch. | No scouting necessary. |
| 575-749 | Eggs begin to hatch. | No scouting necessary. |
| 750-1299 | Young caterpillars begin boring into grass and weeds. | No scouting necessary. Avoid spraying grass and weeds along field edges. |
| 1300-1399 | 10% of caterpillars begin moving into adjacent corn. | Begin scouting field edges for defoliation. |
| 1400-1700 | 50% of caterpillars moving into adjacent corn. | Continue scouting for defoliation along field edges. Spray if necessary. |


