Growing Wheat
All Growing Wheat Content

2018 Field Plot Summaries for Wheat Disease Management Trials
The wheat disease management field experiments conducted in the 2018 growing season evaluated several experimental and commercially available fungicides for managing foliar, head or root diseases of spring wheat. Foliar and spike/head diseases incidence and severity were assessed. The field experiments were implemented at Volga Research Farm and Northeast Research Farm (NERF) near South Shore, SD. Results of the same experiment may vary between Volga and Northeast due to environmental differences between the two locations.

Implications of Excessive Soil Moisture for Disease Development in Winter Wheat
Although it is too early to start thinking about disease issues in winter wheat at this time, current flooding in some areas may have implications on diseases that may develop on winter wheat.

Winter Wheat Breaking Dormancy Early
A threshold indicator for winter wheat emergence is to consider average temperatures over a 14-day period. When that 14-day average temperature is equal to or above 5°C, or 41°F, then hard red winter wheat can break dormancy.
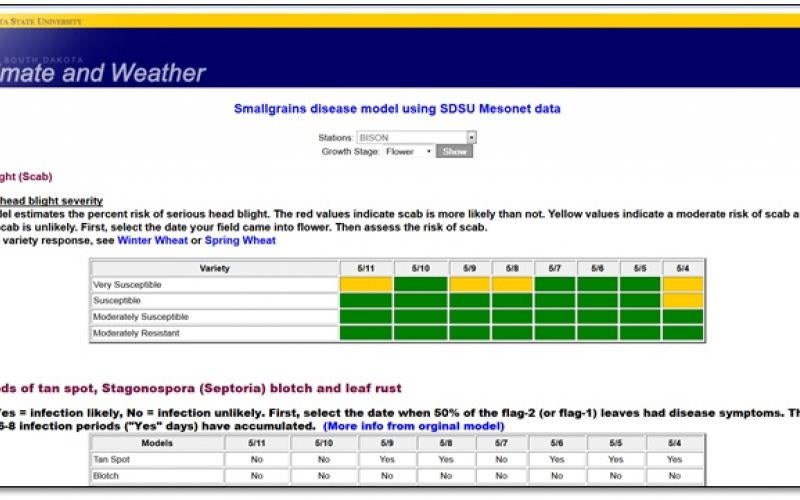
The Small Grains Disease Forecasting System Could Save Producers Money
The South Dakota State University Small Grains Plant Pathology program has partnered with the Small Grains Plant Pathology program at North Dakota State University to deploy a small grains disease forecasting system for South Dakota. The system uses weather variables including rainfall, temperature, and relative humidity to predict the likelihood of disease development. This new tool has the potential to save growers money by helping them avoid unnecessary fungicide applications, or knowing when to apply a rescue fungicide treatment.
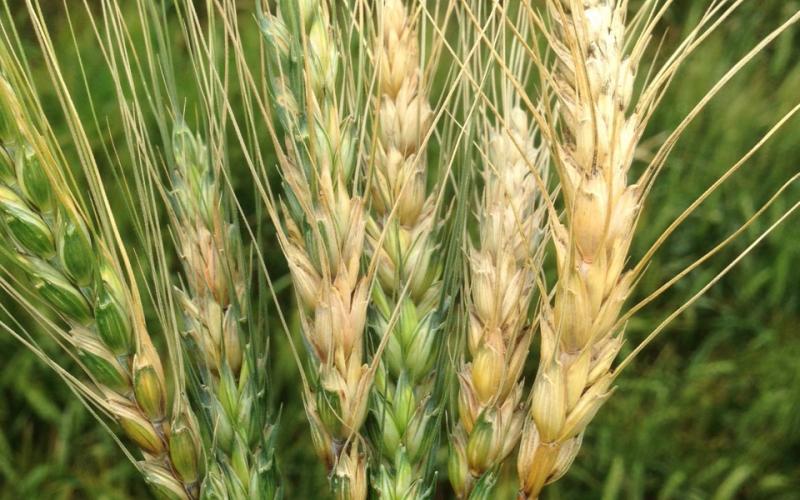

Updated National Fusarium Head Blight (Scab) Prediction Center
The new Fusarium (Scab) Head Blight Prediction Center is now up and running. The purpose of this Assessment Tool is to provide producers and crop consultants with a Fusarium Head Blight (FHB/scab) risk assessment tool which leads up to and includes flowering (anthesis).
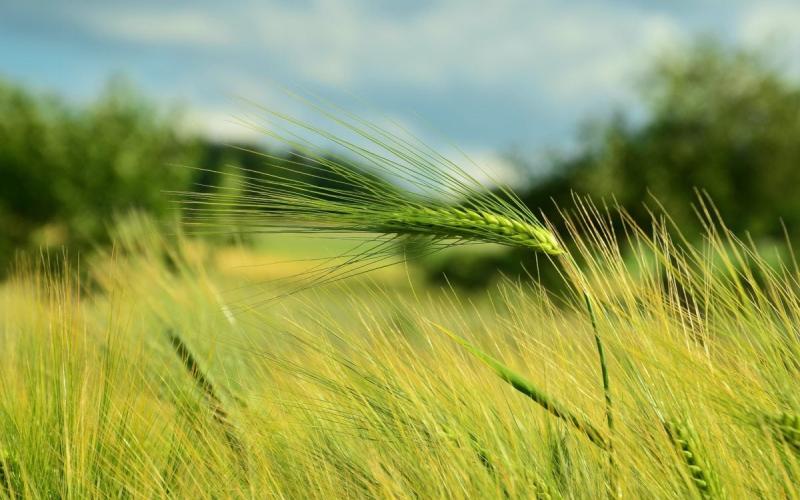

Scouting Wheat Fields
Scouting is the process of monitoring fields and crops during a growing season. It can provide producers with field specific information on pest pressure and crop injury.

Water Use by Plant Stage
Over the growing season, solar radiation, air temperature and plant size are the dominant factors in determining evaporative demand and the rate of water use by wheat. Water use can vary dramatically on a day-to day basis, depending on climate and wheat health.
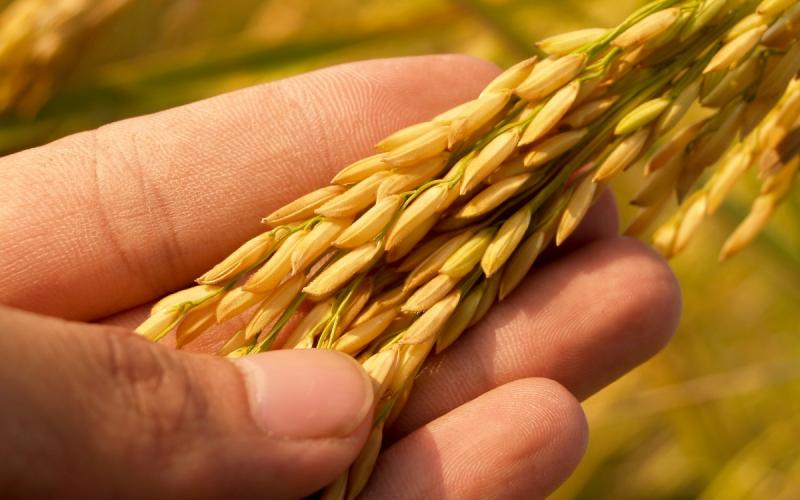

Improving Protein Content in Wheat
Wheat producers in South Dakota always strive to grow a premium product. Quality in wheat often depends on test weight and protein content.

Planning for Quality in Wheat
Excess moisture and limited field days have made it difficult for producers to add nitrogen to wheat fields this year. This could be a concern, as nitrogen contributes to both yield and protein. This year, it may pay off to take tissue and soil tests from questionable wheat fields to help with nitrogen application decisions.

Winter Wheat Planting Considerations
As we move into fall, winter wheat growers often ask, "What is the best time to plant winter wheat?" If planted too early, winter wheat can develop disease and insect problems. If planted too late, it can get winter killed.