Search
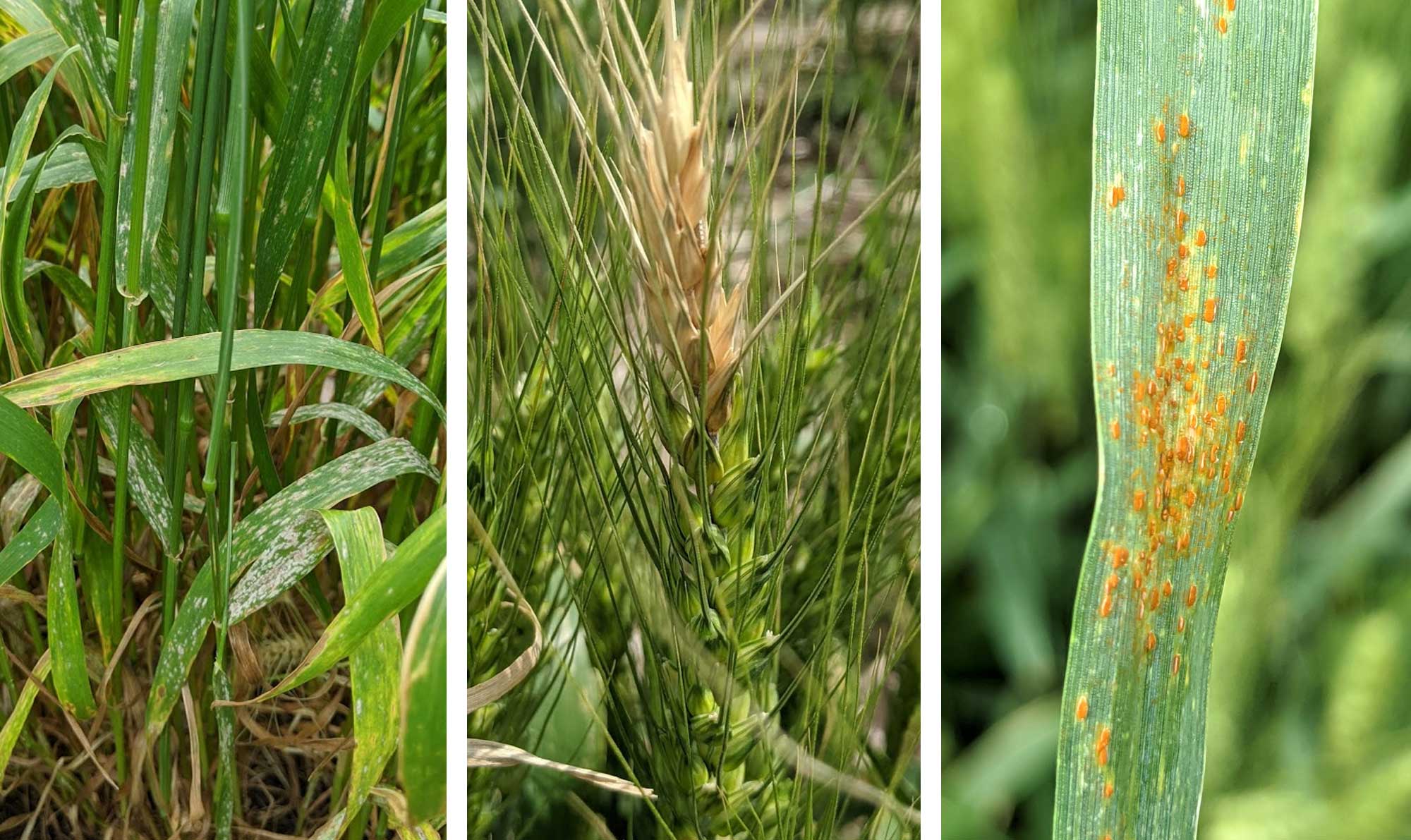

Winter Wheat Diseases Update
Powdery mildew, fusarium head blight and leaf rust were observed in a few winter wheat fields recently scouted. The recent rainfall showers and warm temperatures have favored these diseases to develop in winter wheat.
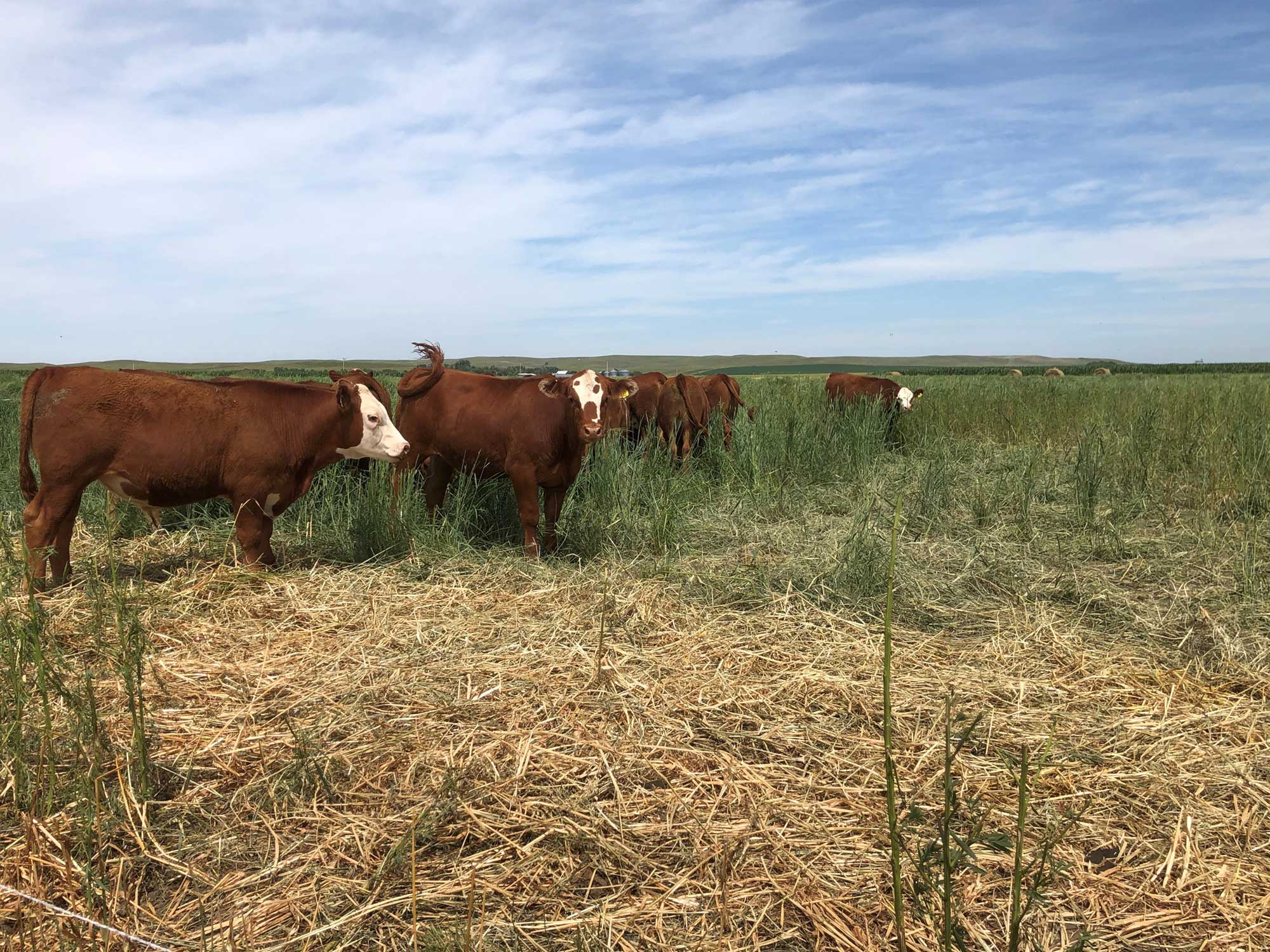

Integrating Perennial Crops in Annual Crop Rotations
The Dakota Lakes Research Farm is working to develop cropping systems that include perennial crops, such as switchgrass, big bluestem and alfalfa, to improve long-term soil health and farm productivity.
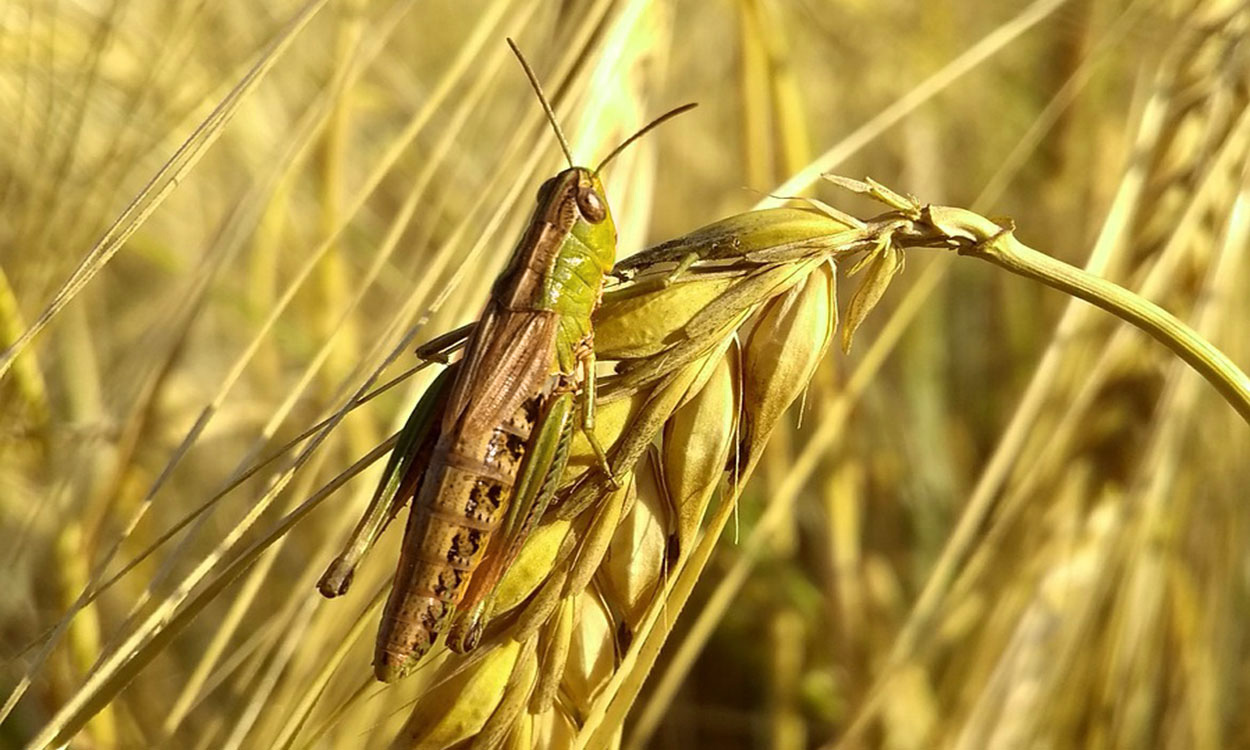

Grasshoppers Are Causing Concerns in Close-to-Harvest Winter Wheat
During the end of last week, we received reports of grasshoppers feeding on winter wheat that was close to being ready to harvest. One of the questions with the report was, “What insecticide can be sprayed that won’t delay harvest?”
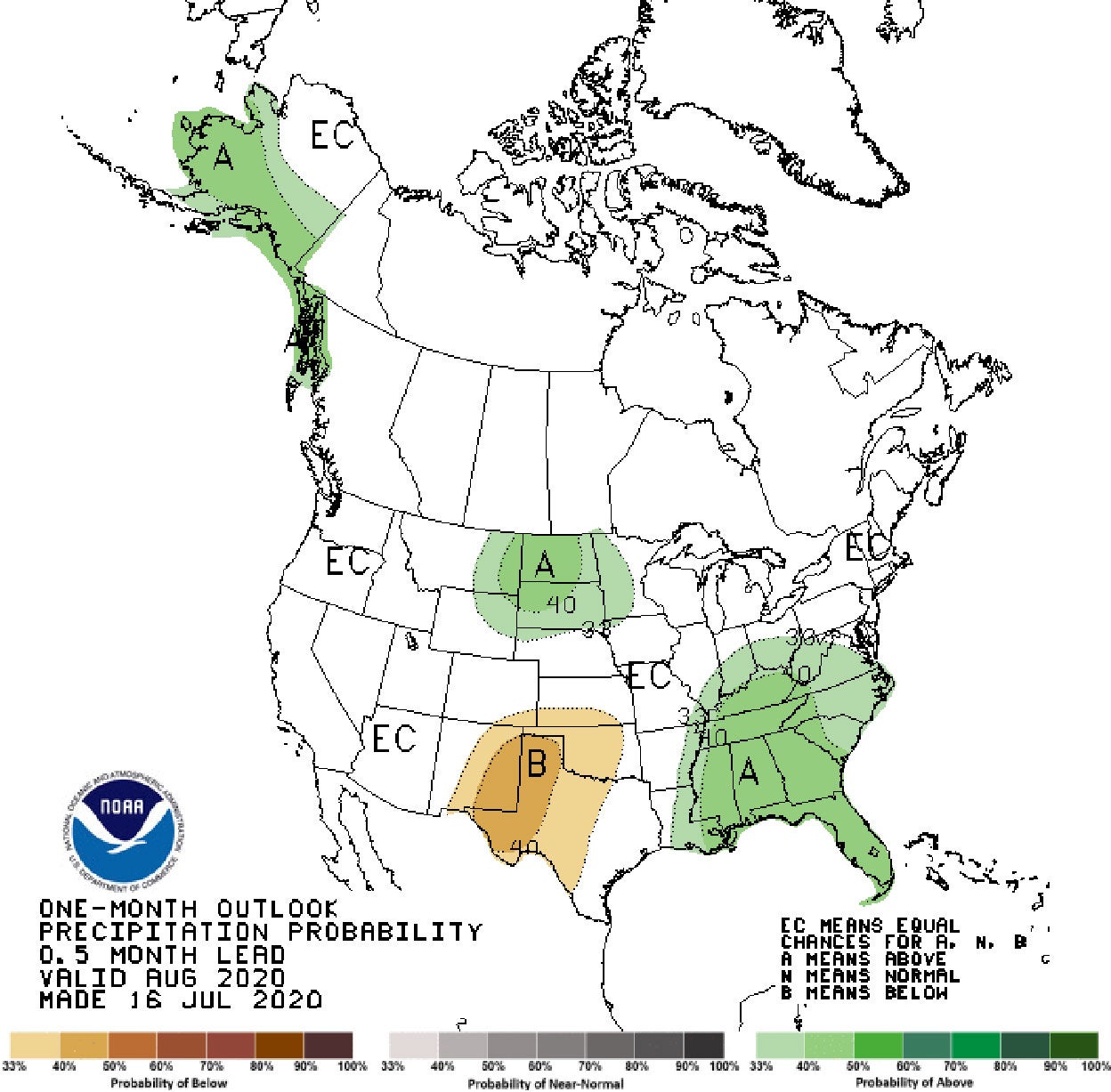
Late Summer 2020 Climate Outlook
Drought concerns in South Dakota may be relieved later this summer, according to the NOAA Climate Prediction Center’s seasonal outlook released this week.
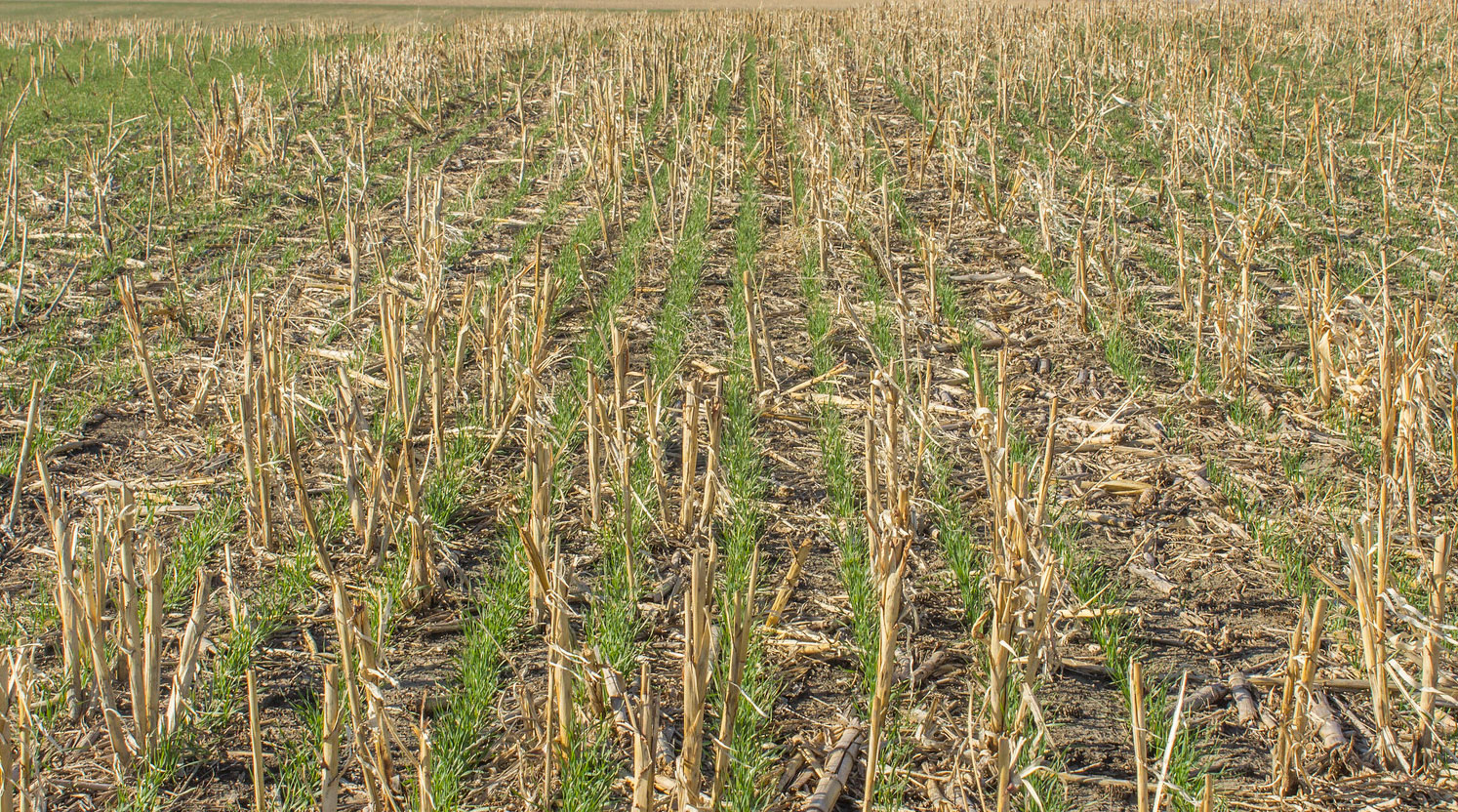

Planting Spring Wheat Into Corn or Milo Residue: Considerations for Scab
Due to current grain prices and other reasons, growers may be considering planting spring wheat into fields that were planted to corn or milo last season. While this type of crop rotation is not generally recommended, economic and logistical challenges sometimes may dictate otherwise.
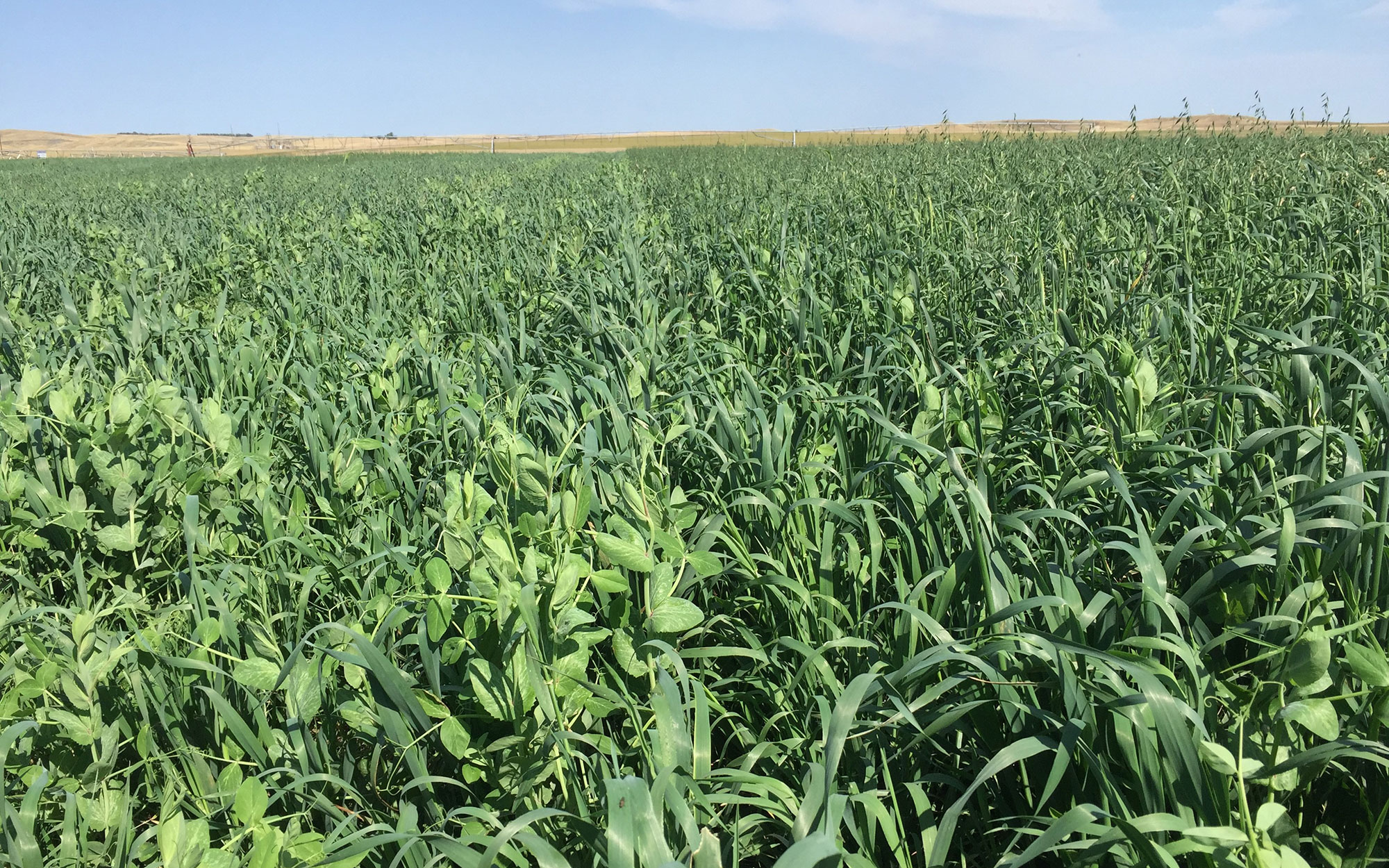

Peas Offer Options in 2020
Current events have made decisions around crop options very difficult this spring. Field peas are an option that may have a fit for some producers.

Fertilizing Forages in South Dakota
Spring is a busy time for South Dakota farmers and ranchers with planting, calving, and other field preparations. Soil sampling and fertilizing pastures, alfalfa, or other forages might be overlooked.
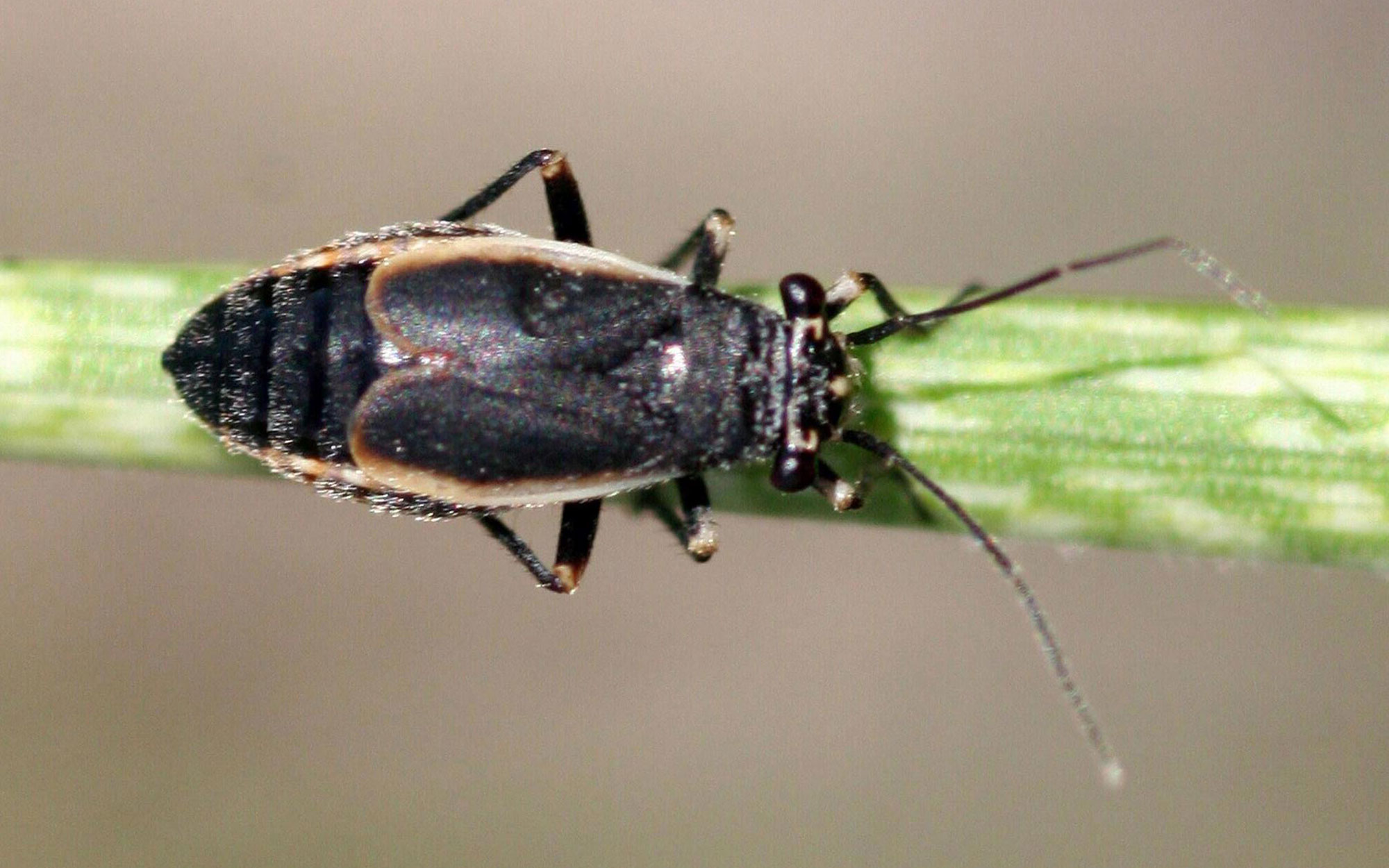

Black Grass Bug Activity Expected in Coming Weeks
Spring green-up is the time to be watching for black grass bug activity. Large populations of this early-season pest can cause severe damage to pasture (up to 90% forage reduction) and infest the edges of wheat fields.
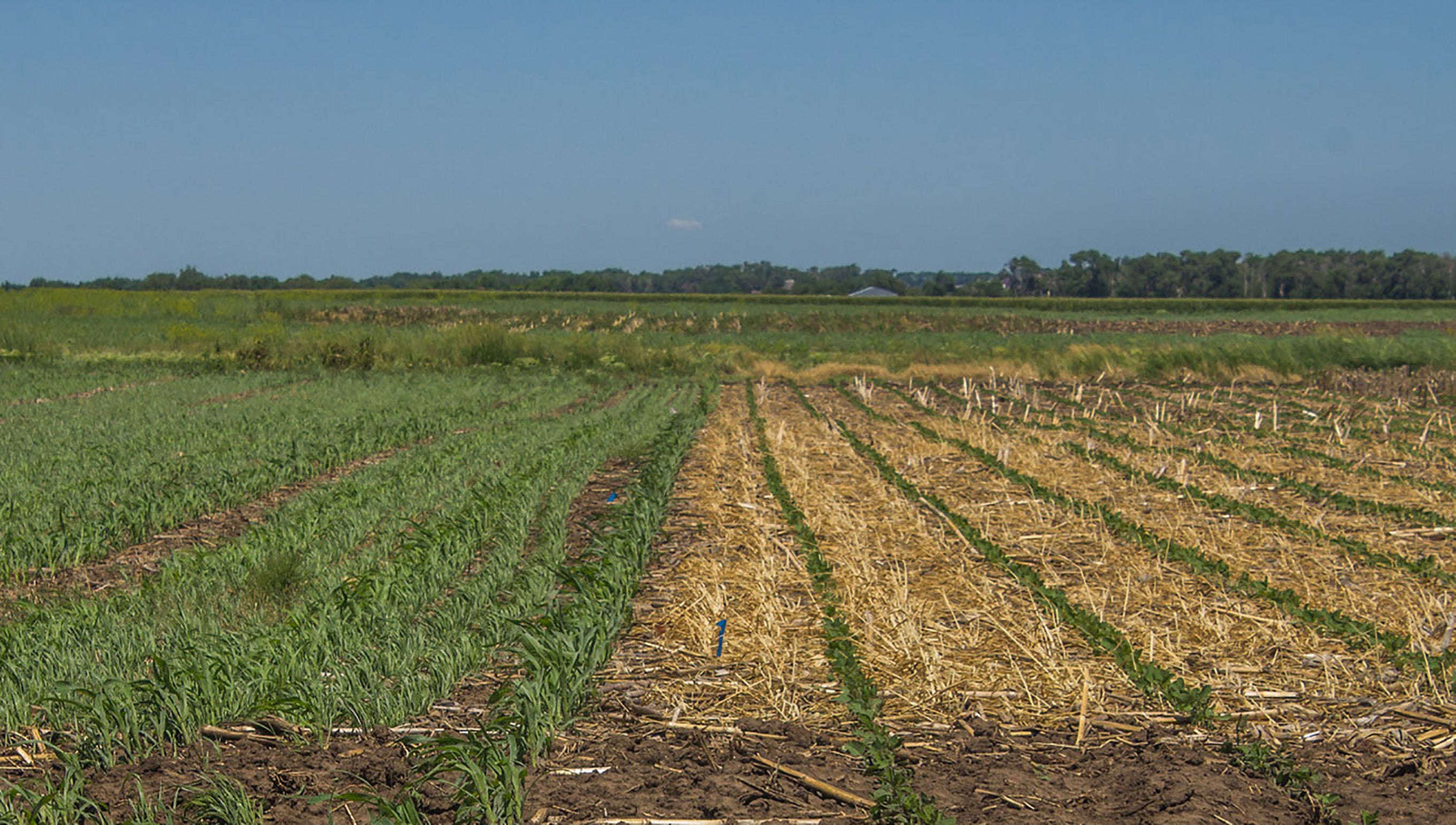

Crop Residue, Cover Crops Impact on Soil Health Parameters
Interest in no-till and cover crops has been on the rise among South Dakota crop producers. In 2019, half of South Dakota crop ground was under no-till management and about 900,000 acres were planted to cover crops.
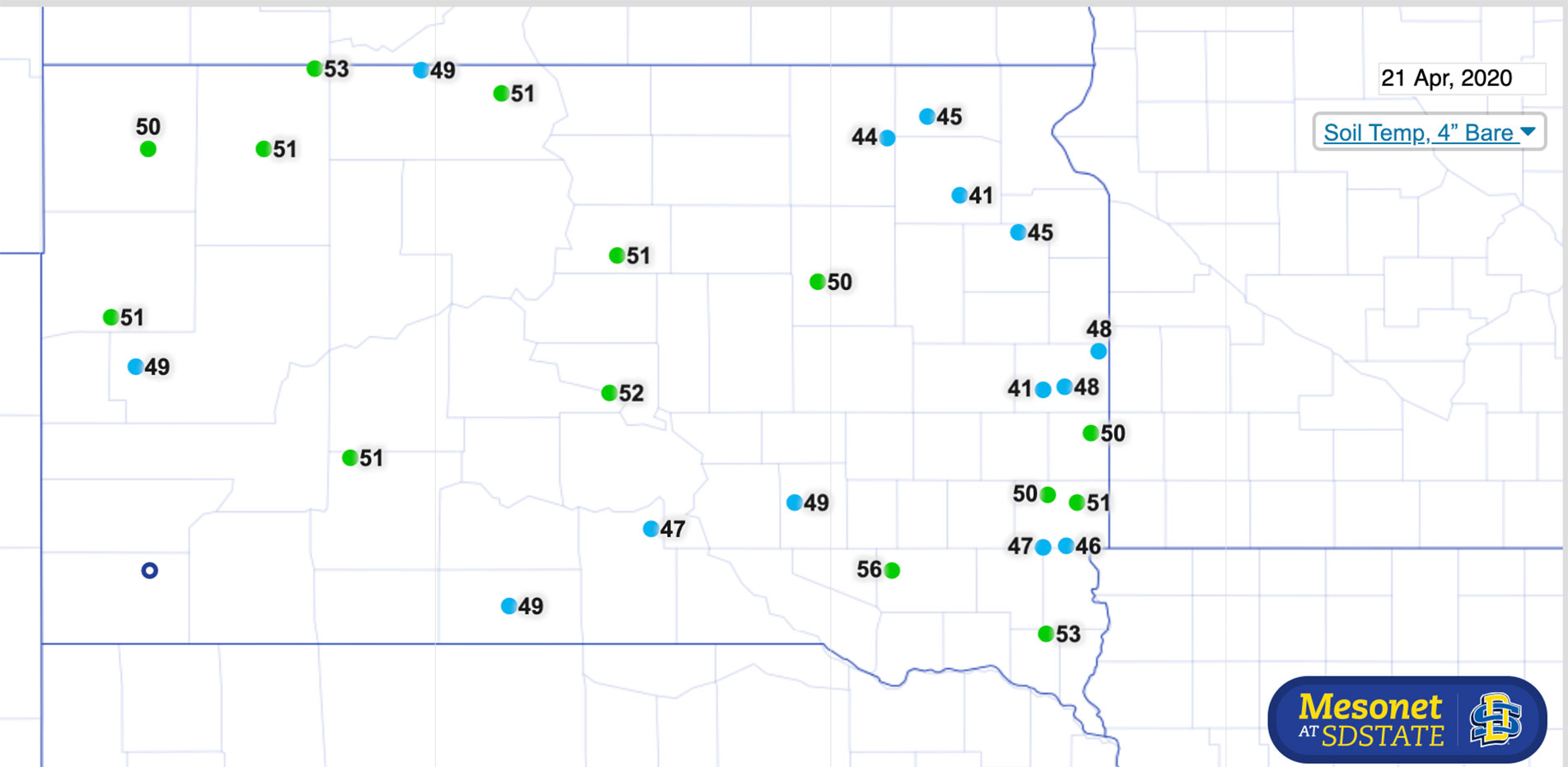
Soil Temperature for Planting Spring Crops
Soil temperature is an important consideration for deciding when to begin planting spring crops. If producers in South Dakota would like a quick reference for soil temperatures in their area, the SD Mesonet network measures soil temperature at several weather stations throughout the state.